
Computer networking is a core part of the whole information technology field because without it computers can never communication with each other locally and remotely. Computer network is required for the data transmission, resources sharing and the communications among the employees of an organization.
To share data and network resources among the computers in a network is known as networking. There are different standards, protocols, devices and applications that form computer network architecture. Following is the basic review of the important things that are involved in the data communication system.
LAN, MAN and WAN are the most common types of the computer network.
The commonly used devices are the routers, switches, bridges, brouter, modems, Ethernet card and hubs. A network can be implemented by the following two methods.
• Wired
Wired networks require the physical cables (UTP/STP, Coaxial cable or fiber optic), HUB/Switch, Server operating system and the LAN card in every computer.
• Wirelessly
Wired networks are ideal for the locations where cluttered wires are not possible and the data and resources are shared without the use of cables. It requires the wireless router, Access point, PCMCIA LAN card in every computer. Wireless communication mediums are radio waves and microwaves.
Network Technologies
Today, a large number of worldwide businesses depend on the computer network technologies like Ethernet, VPN, IP Telephony and storage area networking.
Gigabyte Ethernet
Gigabyte Ethernet is a standardized network technology, which describes the Ethernet systems to operate at 1000 mbps. Gigabyte Ethernet is a fastest Ethernet standard and they allow the data transfer at one gigabyte per second.
LAN Switching
LAN Switching is a local area network technology that provides the maximum bandwidth and this technology is being used to resolve the network congestion, bottleneck and other performance related issues. Switching is the technology that reduces the traffic and increase the bandwidth and the switches that are used are known as LAN switches.
VLAN
VLAN ( Virtual Local Area Network), is a logical entity and its configurations and creation is controlled through the software. VLAN is required if you have more than 200 devices in your LAN and lot of broadcast traffic and divide the network into the different logical segments to have the optimized performance. It controls the bandwidth and offer the high performance and security to your LAN.
Routing
Routers are used as a most important component in the WAN and they can be hardware or software based. Routing carry out the two important tasks in a network i.e. they select the best shortest path and they transmit the information packets across that path. Routers communicate with each other and maintain the routing table.
Routing is a process of moving the data (packets) through an inter network. Routing performs the two basic tasks. Define the paths for a packet and then forward the packets on the basis of defined paths. Routing can also be defined as the communication between two or more logically and physical networks and this communication (packet transfer) is brought by a router.
Routing in the Internet
Routing is the method in which data finds its destination from one computer to the next. In the Internet there are 3 major aspects of routing.
1. Physical Address Finding
2. Determination of inter network gateways
3. Numeric and symbolic Addresses
Physical address finding is the method of the Internet Routing and is used when datagram is transmitted from a computer. It is necessary to encapsulate the IP datagram. This encapsulation requires the local network or physical address.
If a computer wishes to transmit IP datagram it needs to encapsulate the physical address of the destination network device in the frame. This address can be achieved by using the table that will map the IP address with the physical address. Such table can be configured into a file that can be read into the memory at the boot up time. Computer normally uses the Address Resolution Protocol (ARP), which operates dynamically to maintain the translation table.
The second method is necessary because the Internet consists of a large number of local networks, which are interconnected with each other by gateways. Such gateways are known as routers, which has physical as well as logical connectivity with many networks.
The determination of the best suitable gateway and port for a particular IP address is called routing.
The third method generally involves the translation of the human friendly form (names) to the number address (IP Address). IP address can’t be remembered due to its numeric form but the simplest names (domain names) are easy to remember e.g www.yahoo.com, www.google.com, www.msn.com are easiest to remember as compared to the IP addresses 122.11.22.34, 223.45.66.76, 155.44.55.120. DNS translates the domain names into the IP address and IP address into the domain name. This domain to IP translation is a must for communicating on the Internet because communication on the Internet is performed by the IP addresses.
What is Network Routing
Routing is the process of defining routes for the packets to its destination through a internetwork and this is performed by the router. Routing is consist of two separate tasks.
1. Defining paths for the packets through and internetwork.
2. Forwarding data packets based on their predefined paths.
Generally, there are two types of routing.
STATIC AND DYNAMIC ROUTING
Routing can be performed by manually defining the routes or paths for packets to reach its destination. This is called static routing. Stating routing works well for the small networks and when using the static routing, the routing table of the each router should be updated each time there is any change in the network configuration or topology. A router, whose routing table is not regularly updated, cannot communicate with the other routers.
While on the other end in most of the networks, routing is accomplished through the use of the dynamic routing. In the dynamic routing, routing protocols, such as RIP, OSPF etc create and maintain the routing tables of each router. Practically, dynamic routing functions very well than the static routing.
ROUTING TABLE
A routing table is a set or rules, viewed in a tabular format and this used to define the routes of the data packets. All the network devices, which have IP, enabled functionality such as routers and switches use the routing tables. Routing table stores the information and configurations of every router in the IP enabled network. A routing table contains the information necessary to transmit the packets toward its destination.
When a packet is received, the network devices matches the information contained in the packets and the information in the routing tables and then it defines the shortest possible route for the transmission of the packets towards its destination.
Each packet contains the information of its origin and destination and the routing table contains the following information.
• Destination: The IP address of the packet’s final destination (next hop). Next hop: The IP address to which the packet is forwarded
• Metric: It assigns the cost to each route so that most-effective paths can be picked up.
• Routes: It includes directly attached direct subnets, indirect subnets, that are not directly connected to the device but it can be accesses through one ore more hops
• Interface: The outgoing network interface the device should use when forwarding the packet to its final destination.
Routing tables can be maintained manually by the network administrator or by dynamically (automatically). The static network tables do not change unless the network administrator changes them. Routing tables can be maintained manually or dynamically.In the dynamic routing, the network devices such as routers and switches maintain the routing tables dynamically by using the routing protocols, such as RIP, OSPF etc. In the dynamic routing, the network devices listen and detect any network or devices failure and packet congestions.
Communication between Routers
The Internet consists of large number of autonomous systems, each of which further consists of routing domains. Such autonomous systems are usually run by the larger companies or universities. Within the Autonomous system, a router communicates with the other router using the best intra domain routing protocols, which are known as interior gateway protocols. Autonomous system are connected via gateways, these exchange information using inter domain routing protocol, which are also called exterior gateway protocols.
The RIP or (Routing Information Protocol) is the commonest interior gateway protocol and the recent protocol such as open shortest path first (OSPF). The purpose of these protocols is to enable routers to exchange locally so that all the routers in the autonomous system must a have coherent and up to date information.
When a host receives the new routing information, it is likely to update not only to it but also sends this new updated information to all the connected hosts so that they can updated themselves. Hence these changes propagate across the entire network.
Router Commands Overview
There are hundreds of commands of a router.
Keyboard Shortcuts :
CTRL-N - show next command
CTRL-P - show previous command
SHIFT-CTRL-6 – Break
Configuring the Router
You will be able to learn the basic commands for configuring a router:
sh running-config - details the running configuration file (RAM)
sh startup-config - displays the configuration stored in NVRAM
setup - Will start the the automatic setup; the same as when you first boot the router
config t - use to execute configuration commands from the terminal
config mem - executes configuration commands stored in NVRAM; copies startup-config to running-config
config net - used to retrieve configuration info from a TFTP server
copy running-config startup-config - copies saved config in running config (RAM) to NVRAM or "write memory" for IOS under ver.11
copy startup-config running-config - copies from non-volatile (NVRAM) to current running config (RAM)
boot system flash
boot system tftp - tells router which IOS file on the tftp server to boot from
boot system rom - tell router to boot from ROM at next boot
copy flash tftp - Copies flash to tftp server
copy tftp flash - Restores flash from tftp server
copy run tftp - Copies the current running-config to tftp server
copy tftp run - Restores the running-config from tftp server
General Commands
no shutdown - (enables the interface)
reload - restarts the router
sh ver - Cisco IOS version, uptime of router, how the router started, where system was loaded from, the interfaces the POST found, and the configuration register
sh clock - shows date and time on router
sh history - shows the history of your commands
sh debug - shows all debugging that is currently enabled
no debug all - turns off all debugging
sh users - shows users connected to router
sh protocols - shows which protocols are configured
banner motd # Your customized message here # - Set/change banner
hostname
clear counters - clear interface counters
Privileged Mode commands of a router
Learn how to work in the privileged mode of a router.
enable - get to privileged mode
disable - get to user mode
enable password
enable secret
Setting Passwords on router
Here you will be able to learn how to set the password on a router.
enable secret
enable password
Setting the password for console access:
(config)#line console 0
(config-line)#login
(config-line)#password
Set password for virtual terminal (telnet) access (password must be set to access router through telnet):
(config)#line vty 0 4
(config-line)#login
(config-line)#password
Set password for auxiliary (modem) access:
(config)#line aux 0
(config-line)#login
(config-line)#password
Router Processes & Statistics
By these command you can see the statistics and different processes of the router.
sh processes - shows active processes running on router
sh process cpu - shows cpu statistics
sh mem - shows memory statistics
sh flash - describes the flash memory and displays the size of files and the amount of free flash memory
sh buffers - displays statistics for router buffer pools; shows the size of the Small, Middle, Big, Very Big, Large and Huge Buffers
sh stacks - shows reason for last reboot, monitors the stack use of processes and interrupts routines
IP Commands
Here is a list of the IP Commands
Configure IP on an interface:
int serial 0
ip address 157.89.1.3 255.255.0.0
int eth 0
ip address 2008.1.1.4 255.255.255.0
Other IP Commands:
sh ip route - view ip routing table
ip route
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0
ip classless - use with static routing to allow packets destined for unrecognized subnets to use the best possible route
sh arp - view arp cache; shows MAC address of connected routers
ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.0 secondary - configure a 2nd ip address on an interface
sh ip protocol
CDP Commands (Cisco Discovery Protocol uses layer 2 multicast over a SNAP-capable link to send data):
sh cdp neighbor - shows directly connected neighbors
sh cdp int - shows which interfaces are running CDP
sh cdp int eth 0/0 - show CDP info for specific interface
sh cdp entry
cdp timer 120 - change how often CDP info is sent (default cdp timer is 60)
cp holdtime 240 - how long to wait before removing a CDP neighbor (default CDP holdtime is 180)
sh cdp run - shows if CDP turned on
no cdp run - turns off CDP for entire router (global config)
no cdp enable - turns off CDP on specific interface
IPX Commands :
Enable IPX on router:
ipx routing
Configure IPX + IPX-RIP on an int:
int ser 0
ipx network 4A
Other Commands:
sh ipx route - shows IPX routing table
sh ipx int e0 - shows ipx address on int
sh ipx servers - shows SAP table
sh ipx traffic - view traffic statistics
debug ipx routing activity - debugs IPS RIP packets
debug ipx sap - debugs SAP packets
Routing Protocols :
RIP, IGPR and OSPF are the routing protocols and here is a list of the commands for the working on the routing protocols.
Configure RIP:
router rip
network 157.89.0.0
network 208.1.1.0
Other RIP Commands:
debug ip rip - view RIP debugging info
Configure IGRP:
router IGRP 200
network 157.89.0.0
network 208.1.1.0
Other IGRP Commands:
debug ip igrp events - view IGRP debugging info
debug ip igrp transactions - view IGRP debugging info
Access Lists
Here is a list of the Access list command of a router.
sh ip int ser 0 - use to view which IP access lists are applies to which int
sh ipx int ser 0 - use to view which IPX access lists are applies to which int
sh appletalk int ser 0 - use to view which AppleTalk access lists are applies to which int
View access lists:
sh access-lists
sh ip access-lists
sh ipx access-lists
sh appletalk access-lists
Apply standard IP access list to int eth 0:
access-list 1 deny 200.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
access-list 1 permit any
int eth 0
ip access-group 1 in
Apply Extended IP access list to int eth 0:
access-list 100 deny tcp host 1.1.1.1 host 2.2.2.2 eq 23
access-list 100 deny tcp 3.3.3.0 0.0.0.255 any eq 80
int eth 0
ip access-group 100 out
Apply Standard IPX access list to int eth 0:
access-list 800 deny 7a 8000
access-list 800 permit -1
int eth 0
ipx access-group 800 out
Apply Standard IPX access list to int eth 0:
access-list 900 deny sap any 3378 -1
access-list 900 permit sap any all -1
int eth 0
ipx access-group 900 out
WAN Configurations Commands
Networking over WAN is the main functionality of a router. The most common use of a router is for the WAN connectivity.
PPP Configuration
Point to point protocol is a method for the WAN connectivity and you will find here some commands of PPP.
encapsulation pppppp authentication
ppp chap hostname
ppp pap sent-username
sh int ser 0 - use to view encapsulation on the interface
Frame-Relay Configuration
One of the methods for the WAN connectivity is the Frame Relay. Find here some basic commands for the WAN connectivity through Frame Relay.
encapsulation frame-relay ietf - use IETF when setting up a frame-relay network between a Ciscorouter and a non-Cisco router
frame-relay lmi-type ansi - LMI types are Cisco, ANSI, Q933A; Cisco is the default; LMI type is auto-sensed in IOS v11.2 and up
frame-relay map ip 3.3.3.3 100 broadcast - if inverse ARP won't work, map Other IP to Your DLCI # (local)
keep alive 10 - use to set keep alive
sh int ser 0 - use to show DLCI, LMI, and encapsulation info
sh frame-relay pvc - shows the configured DLCI's; shows PVC traffic stats
sh frame-relay map - shows route mapssh frame-relay lmi - shows LMI info
Miscellaneous Commands
In the last but not least here is a list of the some miscellaneous and useful commands
sh controller t1 - shows status of T1 lines
sh controller serial 1 - use to determine if DCE or DTE device
(config-if)#clock rate 6400 - set clock on DCE (bits per second)
(config-if)#bandwidth 64 - set bandwidth (kilobits)
VPN (Virtual Private Network)
A VPN stands for virtual private network and it is a communication network that is tunneled through another network usually internet. VPN can link the enterprise offices, reduce the operation cost, allow customization of security and quality of service and provide the secure communication by using the Point to Point Tunneling Protocol, PPTP, L2TP, SSL and IP sec. VPN can be used in the home, small offices and in the enterprises.
A virtual private network is a private network that uses public network (Internet) and maintains privacy and security procedures through encryption and other security procedure. VPN’s provides an alternative dedicated private network connection for the offices and companies.
Many businesses around the world are using VPN to connect their office servers from other locations such as home etc. Virtual Private Network uses PPTP (Point to Point Tunneling Protocol to allow Windows and Mac users to connect to the PowerElf servers from the other locations.
PPPT provides a secure 128bit encrypted connection from the local computer to the VPN server. In VPN, not only the data is encrypted but the source and destination network address is also encrypted.
VPN uses internet as a medium to connect to the remote networks and sites and allows virtual connections.
Virtual Private Network is an alternative method to connecting the office network or a LAN. Internet is a public domain and anyone with a computer, a phone line, modem and internet service can access it.
VPN uses a set of the security methods, such as encryption, passwords, firewalls and other security procedures. VPN may be composed of a number of servers and sites.
The most common Virtual Private Network is a remote-access VPN, which creates a secure tunnel from your computer and your company’s server.
In some cases you don’t even need to have internet access but you only need a computer, telephone line, modem and software, which network administrator might have installed on your computer or you will be provided with the instructions that how to configure PPTP.
After successfully configuring the PPTP, you will be able to dial the company’s server and access it by creating a VPN. In Virtual Private Network, remote computers act as they are in the same and secure local network.
There are a number of advantages and disadvantages of the VPN connections.
Advantages
• It allows and makes you able to connect and access your company’s computer, while you are at your home or other remote location. This is the same way as you access your company’s computers in your office.
• It is almost impossible for someone to interfere or intrude in your VPN network tunnel
• You can even connect to your company’s network from all over the world if you have installed and configured VPN client software on your laptop.
Disadvantages
• The setup of the Virtual Private Network connections is comparatively more complicated than the normal network connections. VPN can work around the network products of different companies but connecting to a non-NETGEAR product will add some difficulty.
You will have to follow the company’s own policies and procedures while connecting to its network through VPN. VPN goes between a computer and network or a local LAN and a remote network using routers. Each end of the connection is an VPN endpoint. The connection between the two VPN networks is called VPN tunnel.
All NETGEAR router supports VPN pass through. Pass through means that a router does not stop VPN traffic. The purpose of VPN is to prevent the data between two computers or networks being altered.
The whole purpose of VPN is to prevent data being altered, so, for example, a pass through router that is also running NAT will break the VPN connection.
VPN Essentials
For setting up the Virtual Private Nework connection you need the basic equipment and the VPN account from your Internet Service Provider. The latest operating systems like Windows 2000, Windows 2003 server or professional does not require the separate VPN client software. But if you have old operating systems like Windows 95/98, you will require additional software for VPN.
Hardware
• PC with the processor speed of more than 300 MHZ.
• RAM: 128MB although 64 MB is the minimum support but it may limits many features and of VPN.
• 1.5 GB available disk space.
• A dial up, cable modem, ISDN or any type of modem is required. The modems with more speed and good for faster transfer of data.
Software
Any Virtual Private Nework client software.
Internet Account
You will require a VPN account with your ISP with a password and dedicated IP address for the security connection and encryption purposes.
Virtual Private Network Accessories
An increasing number of businesses are opting for the VPN solutions. Different vendors are adding the different functionalities in the hardware and software such as encryptors in the hardware. Some are adding security and firewall related capabilities both in software and hardware.
Virtual Private Network Working
There are many aspects of the working of the VPN and it depends on the software, hardware and the architecture of the VPN connection. Each VPN connection type has it own features with respect to security, scalability and quality of service. There are 2 main types of the VPN connections such as individual computer to LAN and LAN to LAN connections.
The purposes of the protocol involves in VPN are as follows. • The encryption of data at the sending end.
• Creation of a tunnel where data in the form of packets is encapsulated in the form of TCP/IPnetwork.
• The decryption of the data at the receiving end.
• Other security measures included password security, firewall and the encryption of the host and remote computers or networks IP address.
IP Telephony
VOIP or IP telephony carry the voice signals over internet or the packet switched networks PSTN. VOIP can transmit more than 1 telephone call through the same broadband connection. Additionally, it provides the 3-way calling, call forwarding, call id, call waiting and other features. VOIP can be integrated with the other audio and video services. VOIP is a location independent service and can be used anywhere in the world with the access of broadband VOIP operator.
Storage Networking
Storage Area Networking or SAN is a network architecture that is designed to attach the remote storage area devices such as disk arrays, tapes and others in such a way that devices seems to be attached locally. SAN uses SCSI protocols for communication between the servers and the remote storage devices. Sharing storage simply the storage administration and you don’t have to physically move from one server to another. SAN uses the fiber channel technology for the faster and reliable access.
Network Architecture
Network architecture can be classified into the following two categories
• Client/Server
In the Client/server model, there is a centralized server (domain controller) that controls and all the computers are dependent on it.
• Peer to Peer
In the Peer to Peer model, there is no centralized server and every computer acts as a server and client and the same time. All the computers are the part of the same workgroup. Workgroup is used in the places where security is not the main concern.
Protocols
Protocols are the communication stands, agreed upon ways and the language, which two computers understand in order to send and receive the data. There are different protocol such as TCP/IP, FTP, DHCP, BOOTP, SNMP, LDAP, RIP, NNTP, PPTP and L2TP. TCP/IP is a suite of protocols that contains a large number of communication protocols.
Topologies
A network can be implemented by different physical layouts and designs, which are known as topologies. The most common topologies are star, bus, mesh, tree and hybrid. Star topology is the most commonly used topology in the Ethernet based LAN.
Benefits of Networking
Computer networking provides a lot of benefits to every type of the organization where two or more computers are used.
• You can connect your entire office with the Internet.
• You can store commonly used files on the shared drives so that other users in your office can access them.
• You can share the software the multiple users in your LAN.
• You can share the resources such as hard disk, printer, scanner, CD/DVD-ROM and internet with the others users.
• With the intra office Email system you can send the emails and pop up messages to your co-workers.
• With the Surveillance software you can monitor the activities of your employees.
• An important message can be conveyed to all the users of your office in seconds.
• You can install and troubleshoot the remote computer.
• You can access your office computer from your home or from the other remote location with your laptop.
• You can interact with your clients, process orders and make long distance calls with the IP telephony.
• All the computers in your office can be monitored, troubleshoot, scanned for viruses and diagnosed from the centralized server computer.
• Computer networking provides you the fast, flexible, secure, cost effective and excellent work experience.
TCP/IP
Protocols are the set of rules, agree upon ways and communication standards that computer and devices use to communication with each other. TCP/IP stands for transmission control protocol/Internet protocol. TCP/IP is the standard protocol for network communication in LAN or WAN. All the devices and applications have to follow to same protocols to make network communication system.
Introduction to TCP/IP
Here you will learn about Tcp ip network overview, data communication, ip addressing introduction, basic protocols, routing in the internet. TCP/IP short for Transmission Control Protocol is a suite of the communication protocols used to connect the hosts on the internet. TCP and IP were developed by a department of defense (DOD) in a research project to connect the number of networks by different vendors to form a big network of networks (the Internet).
It was originally successfully because of the services it gave, which everyone wanted to use such as file transfer, electronic mail, remote logon across a very large number of clients and server system. Several computers in a small network can use TCP/IP to communicate with each other. The IP component of the TCP/IP suites provides the routing between the two locally or remote computers.
IP forwards each packet based on a four byte, 32 bits address. TCP is responsible for verifying the correct delivery of data from the client to server. TCP also supports to detect the errors in the transmission and also triggers the data to retransmit correctly.
TCP/IP is a de facto standard of transferring the data on the network and on the internet. Each network operating systems that have their own protocols must support TCP/IP too. All the computers in a network must follow the rules to communication with each other.
TCP/IP stands for Transmission Control Protocol and Internet Protocol and it is a communication standard that defines how data travels on the internet and how network/communication devices communication with each other.
Inside the TCP/IP
TCP/IP is a not a single protocol but it is a suite of the protocols. There are the numerous protocols in the TCP/IP suite such as TCP, UDP, ICMP, DHCP, IMAP, HTTP, HTTPS, SSL, SMTP and many others.
Internet Protocol is a connectionless protocol that is used to communicate between the two computers. IP does not occupy the communication line between the two computers. With the IP communication, data is broken into the smaller pieces called packets, and these packets communicate between the two locally or remotely connected devices in a computer network or via internet. IP is also responsible for routing the packets to its destination. Routers are responsible for routing the packets towards its destination when a computer sends packets to an IP router. Data is routed towards its destination is all by a router. Router works as a post office.
TCP/IP
The TCP/IP (transmission control protocol/Internet protocol) work together in which TCP takes care communication between the application software i.e browsers whereas IP takes care of the communication between the computers. TCP breaks the data into smaller packets before they can be sent and IP sends the packets to the receivers.
IP Addresses
Each computer in a network or on internet must have a unique IP address before it can communicate with the other computer. The packets must have the address of the destination computers or devices. Each IP address is composed of 32 bits and 4 octets each packet must have an address before it can be sent to another computer.
This is an IP address 100.100.100.10 and this website http://www.example.com might have mapped with the same IP address. Without a unique IP address the communication on the internet is impossible. The numbers in the address must range between 0 and 255 in four period separated portions. Each IP address consists of 32 bits and 32 bits are consisting of 4 bytes. A computer byte can contain 256 different values e.g 00000000, 00100010, 00000111, 11111000, 01010101, 001100110 and up to 11111111.
Domain Names
Domain names are the unique identifier of a website because 12 digits numbers are difficult to remember. The name used for the web address is called a domain name e.g www.google.com, www.msn.com, www.yahoo.com all are domain names and comparatively are easy to remember instead of 12 digits numbers like, 123.220.44.240, 100.100.100.101 and 202.202.56.110. When you type a domain name in your web browser the domain name is translated into IP address by the DNS server, which is managed by your local ISPs or your corporate DNS servers.
All over the world a larger number of the DNS servers are connected with each other some are primary DNS servers, secondary DNS servers, Master DNS servers and Root DNS servers. When a new domain is registered by a domain registrar with associated TCP/IP address then DNS servers from all over the world are updated.
TCP/IP is a large collection of the different communication protocols.
TCP/IP is a large collection of different communication protocols.
A Family of Protocols
TCP/IP is a large collection of different communication protocols based upon the two original protocols TCP and IP. Each protocol in the TCP/IP suite is responsible for the different communication tasks. HTTP is responsible for the communication between the web server and the web browser. It sends requests from the client (browser) to web server and returning the web pages to the client.
HTTPS is responsible for the secure communication between the web browser and the web server. HTTPS usually handles the credit card transactions and other sensitive and secure data. SSL is responsible for the encryption of the data for the secure communication. SMTP (Simple mail transfer protocol) is responsible for sending the emails. MIME (Multi purpose Internet mail extension) is responsible for communicating the multimedia data such as, voice, video, graphics etc. IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol) is responsible for storing and retrieving the emails.
POP (post office protocol) is used for downloading the emails from the email server to the personal computer. FTP (File transfer protocol) it takes cares of transferring the files between the computers. NTP (Network time protocol) is used to synchronize the time between the networks. DHCP (Dynamic host configuration protocol) is responsible for assigning the IP address dynamically to the network computers. SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) is used for administration of a computer network.
LDAP (Light weight directory access protocol) is used for storing the names and email addresses on the internet and also communicating with the Active directory in computer network. ARP (Address resolution protocol) is used to find the hardware address of a computer based on the IP address. Boot P protocol is used for starting computers in a network. PPTP (Point to point tunneling protocol) is used to make a secure tunnel in the private networks such as VPN.
TCP/IP is the Internet Communication Protocol.
A protocol is a set of rules, agreed upon methods or a communication language, which both computers understand and agree upon. TCP/IP defines the rules to communicate over the internet. Internet browsers and Internet servers uses TCP/IP to communicate on the internet
Web browsers, Web servers, Email programs and internet address all follow TCP/IP. An IP address is a part of the TCP/IP protocols.
TCP/IP Network Administration Tips
TCP/IP stands for Transmission Control Protocol and Internet Protocol. TCP/IP is a suite of the Protocols and more than 65,000 protocols are packed in it. TCP/IP provides the platform for the IP based network. IP networks are most the popular networks and administering the TCP/IP networks requires a lot of experience and skills. An IP based network can be composed of two computers or thousands of computers. Bigger the network the more administration and management is required.
Being a person who is responsible for the network and system administration, it’s your responsibility to equip yourself with the all the required skills and tools. Because the lack of skills and necessary software can create problems not only for the single user but for all the network users. Following are the helpful tips for managing and troubleshooting the TCP/IP based network.
TCP/IP Network Administration Tips
• Enable BIOS passwords
• Lock Server Room
• Make sure to have a battery backup to your network servers and computers.
• Install the latest service packs, security patches and critical updates.
• Backup your critical data on from the server on the regular basis.
• Build and update the technical documentation.
• Maintain inventory of the network hardware and software.
• Maintain a good inventory of the troubleshooting, monitoring and security software.
• Monitor the internet activities of the users with the internet filtering software.
• For the optimized performance of the network computers, put restrictions on the users that they can’t install any software program.
Troubleshooting TCP/IP
I have categorized the common types of the problems and their solutions in the TCP/IP based computer network.
Approaching a problem
First troubleshooting step is to approach the problem in a very intelligent way. If a problem occurs, never lose your sense, don’t feel overburden and confused. Just be relaxed and find out that why this particular problem has happened. Is it a security related issue, hardware conflict, DNS error, internet connection problem, performance issue or the network connectivity issue. After finding out the problem you should be equipped with all the necessary tools, software and of course skills.
For example if you find out the problem is due to the viruses, scan your computer with the latest antivirus and anti spyware program. Block the suspicious activities and the web applications that are notorious for the viruses. The other required things for troubleshooting the problems are diagnostic tools, cable testers, protocol analyzers and network monitoring software.
IP Addressing :
Here you will learn about ip address network introduction and general overview of routing, subnet mask, subnetting, data communication. IP address is an identifier for a computer or device on a TCP/IP network and Internet. Networks that use the TCP/IP protocols route traffic based on the IP address of the destination computer or network device. The format of the IP address is 32 bits 4 octets 4 bytes such as 100.100.10.1, 210.100.22.30, 1.10.1.2 these are the examples of the IP address. The format is a 32-bit numeric value written as four numbers and separated by periods.
Each number in the IP address can be between 0 and 255. In your private network, you can assign unique IP address randomly. However, when you want to connect your private network to the Public network such as Internet then you must need a registered IP address to communicate on the internet and to avoid duplicate address. The four numbers in an IP address are used in different ways to identify a particular network. The general internet registries such as APNIC, RIP, NCC and LACNIC assigns internet or IP addresses from the following 3 classes.
1. Class A- IP address from 0-126. It supports 16 million hosts and 126 networks.
2. Class B- IP address from 128-191. It supports 65,000 hosts and 16,000 networks.
3. Class C-IP address from 192-223. It supports 254 hosts and 2 million networks.
The number of unassigned IP address is running out and a new classless scheme called CIDR is replacing the classes based system of the IP address. In this system the A, B and C class is tied to adoption of IPV6.
Every device connected to the Internet must need a unique identifier, which is called an IP address. An IP address is a numeric value separated by periods into four octets. These numbers are usually assigned to the ISPs (internet service providers) within region-based blocks. An IP address can be used to identify a region or a country. An internet user’s geographical location can be determined with the help of an IP address. The number system is generally difficult to remember so the IP address may also assign to a Host name.
The host names are usually easy to remember. In simple words, every website on the internet must bound or mapped with an IP address. At one time ISPs usually issue one IP address to each user. Within each ISP a DHCP (Dynamic host configuration protocol) server is configured, which dynamically assigns IP addresses from a given pool to each user who connects to the ISP. Dynamic IP addresses also limit the ability of a user to host websites, mail servers, ftp server, mail server and web portals.
Understanding IP Addresses Scheme
An IP address is an address that is used to uniquely identify a device or computer on an IP-based network. An IP address is an address used to uniquely identify a device on an IP network. An IP address can be divided into two parts network portion and a host portion. Each IP address is associated with a subnet mask. The 32 bit address is broken into 4 octets and 1 octet=8 bits. Each octet is converted to a decimal and is separated by periods.
For example 0000000000.11111111.00000000.11111111 this is a binary representation of an IP address. Each octet’s decimal value ranges between 0 and 255. The binary octets convert into decimal value. Here you can see that how a binary octet converts into decimal value. The right most bit or least significant bit of an octet will hold a value of 20.
The bit left to that bit will hold a value of 21. This process continues until the left most bit or the most significant bit holds the value of 27. If all the binary bits are one the decimal representation will be like this.
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
128 64 32 16 8 4 2 1 (128+64+32+16+8+4+2+1=255)
Now here is a sample conversion of the octet if not all the bits are set of 1.
0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1
0 0 32 0 0 0 0 1 (0+64+0+0+0+0+0+1=33)
In the following example you can see the IP address representation both in binary and decimal values.
64. 2. 135. 19 (decimal)64+2+135+19=220
01001010.00000010.1000111.00010011 (binary)
The octets are broken down to provide a large number of the addressing scheme that can accommodate small and very large networks. There are five different classes of the IP networks. Class A, B, C, D and E. The classes from A to C and mainly in use, D and E are experimental and reserved so they are not commonly in use. Due to the classless inter domain routing (CIDR) these addresses are not practically in use.
Network/Subnet Masks
A network mask helps you which portion of the address identifies the network portion and the host portion of an IP address. The three different classes of the IP addresses have their own default masks as shown below.
Class Subnet Mask
Class A: 255.0.0.0
Class B: 255.255.0.0
Class C: 255.255.255.0
An IP address on a class A network that has not been subnetted would have an address and subnet mask pair such as 10.111.20.1 255.0.0.0. If you want to know in more detail that how a mask help you identify the network and host part of the address simply convert the IP address and subnet mask into the binary numbers.
4.16.15.1= 00000100. 00010000.00001111.00000001
255.0.0.0 = 11111111. 00000000.00000000.00000000
If you have the address and the subnet mask in the binary forms then identifying the network portion and the host portion is very easy. Any address value that has the corresponding subnet mask binary value set to 1 show the network ID. Any address bit that has corresponding subnet mask value to 0 represents the host ID.
4.16.15.1= 00000100.00010000.00001111.00000001
255.0.0.0 = 11111111.00000000.00000000.00000000
Network id | host id
If you know your IP address of a computer, you can access the services such as online games, FTP, Web and Mail servers, and remote access utilities such as Remotely Anywhere, PCToGo, PCAnywhere, Remote control etc.
How do I change my IP address?
There are a number of methods by which you can change the IP address of your computer.
What is Subnetting?
Here you will find subnet network overview, ip addressing, address translation, network overview, subnet masking and subnetting overview. A subnet or a subnetwork is a separate part of an organization’s network. In a subnet all the machines are typically in one room, building or at one geographical location.
By dividing an organization’s network into the subnets allows it to connect to the internet by using the same shared network address. Without subnet’s an organization may get different connections to access the internet. Subnetting is the modification of a single IP network to create two or more logically different networks.
A subnet allows the flow of network traffic between hosts to be segregated based on the configuration of a network. Subnetting can improve the network security and performance by arranging the hosts into the different logical groups. Subnetting is required when one network address needs to be distributed across multiple network segments. Subnetting is required when a company uses two or more types of the network technologies like Ethernet and Token Ring.
Two network segments are restricted by distance limitations. Submetting or dividing the network into the segments is also required when localized network management is required for example accounting, sales, customer service departments. There is another reason for the subnetting, which is that the computers on the network, which use more bandwidth, needs to be separated from the rest of the computers. There are certain advantages and disadvantages of the subnetting. Before you start dividing your network into the different segments, you should assign the IP address to each computer in your network segment.
Subnetting makes the network management easier and it is also very helpful for the troubleshooting of a network segment. The internet is a collection of networks where users communication with each other. Each communication on the internet carries the source and the destination address of the computer. This address is called IP address. This 32 bit address has two parts: one part represents the network portion and the other part represents the host portion of the IP address. A company can use some of the bits in the machine or host portion of the address to identify a subnet. In this scenario, the IP address contains three parts: the network address, the subnet address and the machine address.
Subnet Mask Basics
The most recognizable part aspect of subnetting is the Subnet mask. A subnet mask contains 4 bytes, 32 bits and is divided into 4 period separated octets. Typically, a very common subnet mask in binary looks like this.
11111111 11111111 00000000 00000000
255 255 0 0
How to Apply a Subnet Mask
A subnet mask does not work like an IP address and it cannot exist separately without an IP address. An IP address and subnet mask work together to form a network. An IP address splits into two main parts when applying the subnet mask. The leftmost bits of a subnet mask must be set to 1. For example
11111111.00000000.00000000.00000000
11111111.11111111.00000000.00000000
11111111.11111111.11111111.00000000
The above example shows the valid representation of a subnet mask into the binary numbers.
00000000.00000000.00000000.00000000 is an invalid subnet mask.
11111111.11111111.11111111.11111111 is also invalid subnet mask.
All valid subnet masks contain two parts: the left side with all mask bits set to '1' (the extended network portion) and the right side with all bits set to '0' (the host portion), such as the first example above.
Subnetting an IP network can be performed for a variety of reasons such as using the different physical media in an organization, such as FDDI, WAN and Ethernet, preservation of the addresses and for the purpose of security, management and ease of troubleshooting. The most
common reason of the subnetting is to control the network traffic. In an Ethernet network, all computers in a segment see all the packets that are transmitted by all the other computers on the same segment.
In this situation, the network performance can be badly affected due to the heavy traffic loads, collisions and the retransmission of the packets. A router is used to connect the IP networks and it also helps to minimize the load of the traffic.
Subnet Masking
By applying the subnet mask to the IP address you can identify the network and host portion of the IP address. The decimal number 1 represents the network portion in the subnet mask and the node is represented the 0s. Performing a logical AND operation between the IP address and the subnet mask resulting in the network address.
For example, using our test IP address and the default Class B subnet mask, we get:
10001100.10110011.11110000.11001000 140.179.240.200 IP address of the class B
11111111.11111111.00000000.00000000 255.255.000.000 Default subnet mask of class B
--------------------------------------------------------
10001100.10110011.00000000.00000000 140.179.000.000 Network Address value
The following example shows the default subnet masks.
• Class A Subnet Mask- 255.0.0.0 - 11111111.00000000.00000000.00000000
• Class B Subnet Mask- 255.255.0.0 - 11111111.11111111.00000000.00000000
• Class C Subnet Mask- 255.255.255.0 - 11111111.11111111.11111111.00000000
Subnetting Review
Subnetting allows network and system administrators some flexibility in defining relationship among the hosts of a network. Hosts on the logically and physically different subnets can talk to each other through specialized devices called gateway or router. The ability to filter the traffic between
subnets can make the more bandwidth availability. Subnetting referred to as subdivision of a class based networks into subnetworks.
A router can exchange subnet routes with the other routers in the network. A subnetted network can’t be split into the isolated portion. All the subnets must be contiguous because the routing information cannot be passed to a non-network member. Router can exchange subnet routes with other routers within the network. Since the subnet masks are identical across the network, the routers will interpret these routes in the same manner. However, routers not attached to the subnetted network can't interpret these subnet routes, since they lack the subnet mask.
Therefore, subnet routes are not relayed to routers on other networks. This leads to our second
restriction. Subnetting allows you to create multiple logically different networks within the same class A, B or C. If you break a major network into smaller networks, it allows you to create a network of interconnecting subnetworks. Any device or gateway that is responsible for connecting the different subnetworks must have the distinct IP address one for each subnetwork.
To subnet a network use and extend the natural subnet mask using some of the bits from the host ID portion to create a subnetwork ID. In this example, given a Class C network of the IP address 4.15.5.0 which has a natural subnet mask of 255.255.255.0, you can create subnets in this manner:
11001100.00001111.00000101.00000000 204.15.5.0
11111111.11111111.11111111.11100000 255.255.255.224
---------------------------------|subnet|----
By extending the natural subnet mask to be 255.255.255.224, you have used three bits from the host portion of the mask and used them to make subnets. By using these 3 bits, it is possible to create 8 subnets. The remaining five ID bits of the host portion, each subnet can make 32 host addresses and the 30 addresses out of 32 are assigned to the devices or computers.
The host IDs of all zeros and all ones are not allowed.
204.15.5.0 255.255.255.224 host address range 1 to 30
204.15.5.32 255.255.255.224 host address range 33 to 62
204.15.5.64 255.255.255.224 host address range 65 to 94
204.15.5.96 255.255.255.224 host address range 97 to 126
204.15.5.128 255.255.255.224 host address range 129 to 158
204.15.5.160 255.255.255.224 host address range 161 to 190
204.15.5.192 255.255.255.224 host address range 193 to 222
204.15.5.224 255.255.255.224 host address range 225 to 254
Communication Devices
There are certain devices that are used in LAN/MAN/WAN and wireless networking. The most important devices are router, switch, hub, modem, NIC adapter, access points, broadband router and communication cables. Hub/Switch is a centralized device in a LAN and all the computers connect with the Hub/Switch. In case of failure of Hub/Switch the whole communication stops. Router routes the traffic to the destination based on the IP address of the source and destination computer. With the help of the routing table, the router chooses the best short possible path for data to be sent to its destination. Wireless routers and access points are used in the wireless networking.
Types of Networking
There are three main types of the computer networking such as LAN, MAN and WAN. A LAN covers a room or a building. A MAN covers a network in a city and a WAN covers wide areas such as in a city, country or a network between two or more countries. A LAN can be wired or wireless, MAN can be wired or Wireless and WAN can be through wireless communication technologies such as ISDN lines, frame relay and ATM.
Wireless Networking
Wireless networks are replacing the wired networks rapidly. The administrative control becomes less due to the removal of the bundle of cables in wireless network. The key components are wireless router, access points and PCMCIA LAN cards.
OSI Layers Model
To understand the communication process make the data communication process standardized, the ISO developed the OSI (open system interconnectivity, which defines the seven layers of the OSI model. These seven layers include Application, Presentation, Session, Transport, Network, Data Link and Physical layer. The detail on the OSI seven layers is covered in the separate topic of this website.
DHCP
DHCP stands for the dynamic host configuration protocol. As we know that a unique IP address is a must for communication in LAN, WAN or internet. Assume you are given the task to assign IP addresses to the 10,000 computers in a network. How would you assign? DHCP answers this questions and it assigns the unique IP addresses to all the computers from a given range. There is an administrative control and you can block, assign, lease, renew, specify duration for the IP address and you also do the many other administrative tasks on the DHCP.
DNS
DNS stands for domain name system. DNS translates (converts) the host name into the IP address and IP address into the host name. One thing is clear that the communication in a LAN private WAN or internet is based on the IP addresses. On internet every IP address is associated with the domain name let’s say assume that the IP address 120.1.1.1. is assigned to www.yahoo.com, 12.1.2.3 is assigned to www.google.com and 35.22.32.5 is assigned to www.msn.com and so on. Just imagine that how many IP addresses you can remember 1, 2, 5, 10, 50, 100 or 1000. IP addresses are actually difficult to remember and domain names are easy so every IP address on the internet is associated with a domain name.
What is DNS
You will learn about the dns server configurations and overview, ip addressing, subnetting, domains description, how ip works. Domain name service is an Internet service that translates domain names into IP addresses. Domain names are easy to remember because they are alphabetic. On the other end, the internet is based on the IP addresses i.e every computer on the internet is associated with a unique IP address.
The communication on the internet is carried out on the basis of IP addresses and not on the domain names. A Domain name server service translates the domain name into its corresponding IP address for example the domain name www.abc.com might be translated to 102.222.34.56. The DNS system is, in fact, forms its own network.
If one Domain name serverserve doesn’t know to translate a domain name, it looks for another one and so on until the exact IP address is returned. DNS translates between the internet names and internet addresses.
How DNS Works
DNS organizes the hostnames in the form of hierarchy. A domain is a collection of of the sites that are related because they form a network (all computers that are geographically close as well. Universities are commonly grouped in .edu domain with each university or college using a separate sub domain.
While most of the topic does not require much technical knowledge, there is one technical part of the Domain name server.
When you type a name like example.com in your internet browsers it finds a way to map that name to the internet IP numbers, by which the internet easily reach the example.com computer. For this purpose your computer uses DNS of your Internet service provider company. All internet traffic work on these numbers and the important factor is that the looking up for the name is done by Domain name server.
That computer has a list of the host names/IP address mapping, which is regularly updated by the root DNS. Root DNS servers are the master servers that can help you look up any name. All the root DNS servers copy their own data from the one master server, which is under the control of ICANN. The root servers usually have a list that where you can look for the top level domains like .com, .net, org and .info etc. The ISP sends request for the particular domain name to the root sever and root server directs the request to the master server. In this way, you get the answer with your requested domain name.
IP routing and root servers
The domain lookups go to and from the root servers because main routers on the internet, ISPs and backbones have the list that where to find it.
Domains Description
.edu This domain name is used by the educational institutes like colleges and universities
.com This domain name is used by the commercial institutes/organizations and companies.
.Org This domain is used by the non-commercial organizations.
.net Administrative hosts, gateways and other networks.
.mil This is used by the U.S. military institutions.
.Gov This is used by the government institutes.
.info Used by the Informative sites.
There is a common question that how large is the internet and how Domain name server works. Domain name server simply provides mapping between hostnames and the IP addresses. When you dial in your ISP number and access it how does it get the answer in the form of requested domain name for you. It’s most likely that ISP may not have stored the information (requested site). In this case first the ISP server will send the query to the root-servers. These are the set of very high-powered servers that know all about the top level domains like .com, .org, .net, .info and all the country domains.
So, the ISP’s name server first contact with the root-servers. If the root-servers don’t have the requested information then redirect the request to the GTLD servers for any kind of top level domain and the answers come back to the ISP’s name servers with the requested information. At each step, ISP’s name server caching all the information. The Domain name server is central to the internet because without a domain name systems (DNS) its impossible to communication on the internet.
Wi-Fi
Wireless fidelity is a base band wireless networking technology that provides high speed internet connectivity to the offices and home users.
Wi-Max
Wi-Max is an advance broadband wireless network technology that provides very high speed up to 70 Mbps. Wi-Max is designed for the corporate office, roaming and home users.
Internet is an example of Network
Internet is the largest network in the work. Millions of computers from all over the world are internetworked with each other and are the part of the internet. The resources hosted on one computer in one part of the world such as web pages, songs files, graphics, video files, documents and images are accessible to the users in another part of the world.
Here you will learn about computer network architecture, physical design, logical topology, protocols introduction, communication planning and basic communication technologies. To properly build, maintain and secure a network you should first know that what a compute network is and how data travels through the wired or wireless network. A person with a good networking skills will be able to tell that a network consist of a computer, cables, PRI lines, Routers, switches, NIC cards, PBXs, TIs, fiber optic and Ethernet cables.
A person who have the strong background in the data network must know that a network consists of a server, workstations, routers, hubs, WAN, LAN, fiber optic and Ethernet cables and devices. Both the telecommunication and data communication persons agree that the cabling is an essential part of any computer network.
The simplest definition of the data network is to connect two more computer computers with each other to share data and resources. The network exists in different sizes and shapes, from home networks to WAN networks. Despite the different roles and various sizes of a network you can have some common similarities in all the networks such as protocols, architecture and topology/design.
Computer Networking Tutorials Overview
In this section you will learn about basic networking tutorials, lan, wan, ethernet, wireless technology, basic topologies, internet, intranet, extranet and VLAN technology. Computer networking is the engineering concerned with communication between computers. A general definition of the computer networking is that two or more computers connected together to share data and resources. Two devices or computers are connected together and are separated by a distance of few meters like Bluetooth technology or unlimited such as internet.
Examples of the computer network are LAN, MAN, WAN and internet. Internet is the largest computer network.
Ethernet
Ethernet is a large frame based computer network technology for the local area networks. The name Ethernet comes from physical concept of Ether which defines a number of wiring and signaling standards for the physical layer. Ethernet has been standardized as IEEE 802.3 and its star-topology twisted pair wiring became the most wide spread network type till present. Ethernet technology replaced the old networking technologies such as coaxial cable Ethernet, token ring, ARCNET and FDDI.
In this section you will learn about the lan terminology, basic ethernet networking overview, a general introduction to LAN, introduction to IEEE, lan topologies, wan standards. You can also find these categories in this site such as network tutorials, computer networking guide, what is networking, tech study guides, topologies ,what is data recovery, wireless communication, computer interview questions and network certification. The IEEE standards have been developed by the International Standards Organization (ISO). The Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers (IEEE) in 1985 produced a series of standards for the Local Area Networks, which are called IEEE 802 standards.
These standards have been accepted widely throughout the IT world. One of the IEEE 802 standards, the IEEE 802.3 is known as “Ethernet”. Ethernet is the most widely used LAN technology. Ethernet was developed by Xerox corporations in 1972 and it was the first LAN.
According to the ISO standards allows manufactures to produce the devices and equipments, which are guaranteed to operate anywhere.
The Ethernet in its simplest form uses a passive bus that operates at 10 Mbps. The bus is formed from the co-axial cable, which connects all the PCs in the LAN.
A single LAN may have 1024 attached computers, although in the real practice most LANS have fewer computers than this number. One or more segments of the co-axial cable are attached to end to end to create the Ethernet Cable Segment. Each segment is terminated by 50 ohm resistors.
In today’s IT world the reliable and timely access to the information has become vital. Today coworkers thousands of miles apart from each other can share data, voice, video etc with the fractions of seconds. Similarly a larger number of the coworkers can review the research data simultaneously. The Internet allows businesses to share information and resources with their customers.
Ethernet is a communication protocol that is embedded in software and hardware devices that intended. Ethernet has become the standard computer networking protocol with the help of the Xerox, Intel and Digital
A basic LAN consists of the following components.
• Two or more computers.
• Network Interface card or LAN Card in each PC.
• Ethernet cable (Cat5, UTP/SPT) cable to connect the two computers.
• A hub, switch or router to route or direct the network traffic.
• Software for the communication/computer networking.
A network interface card (NIC) is attached and installed in each PC and is assigned a unique address. An Ethernet cable is used to connect two computers; Ethernet cable has RJ45connectors at both ends. There can be two scenarios 1. Two computers can directly connect with each other or 2. Each computer is directly connected with the hub/switch and hence communication occurs in the network. The hub or switch acts as relay.
Computer Network can be wireless. Despite of using Ethernet cable for the communication, Wireless Network Interface cards use radio waves to communicate with the wireless switch or hub. A small antenna is used in the wireless NICs, switches and hubs. Although the wireless networks are more easy to use as compared to the cabled networks, but more configurations and extra care is required to setup and run a wireless network.
The alternate technologies to Ethernet are “Token Ring”, which is used in the Ring Topologiesnetworks. Token Ring is designed by the IBM and ATM. In ATM networking, devices are connected with each other over a very large distance (thus forms the WAN), and behaves like LANs.
Ethernet is a well established and widely used network standard for small to medium sized Ethernet networks as well as for other networks. Ethernet has been used over the 3 decades and forms a very excellent networking/communication environment.
Ethernet Terms
Ethernet follows a simple set of rules. To understand these rules its important to understand the
following terminology.
• Node – The devices that are attached to the segments are nodes.
• Frame – The nodes (computers or network devices) communicates in the form of short messages that are known as frames. The frames are chunks of information with variable size.
• Segment – A single shared medium is known as a Ethernet segment.
• Medium – The Ethernet devices are attached to a common medium. The frames of the data travel along with that medium. This medium can be coaxial cable. Today most commonly used communication mediums are UTP/STP cable, fiber optic cables.
Frames are analogous in human language. We have some rules for constructed the sentences. The
Ethernet protocol specifies a set of rules for constructing the frames. The frames length varies. Each frame must contain source and destination address for the identification of the recipient and the send of the message. The nodes can be uniquely and easily identified. Each Ethernet devices must have a single unique address.
Compute networking standards has brought a revolution in the network computing and it made the communication very easy and standarized. Now every computer and networking devices has to to follow the same standard to communicate with each other.
Introduction to Network Switching
An Ethernet is a widely accepted network standard through the world. An Ethernet network is generally composed of several interconnected nodes and these nodes are interconnected with the network through the Ethernet Switch. Network Switches provide various benefits to the computer network such as more capacity, speed, bandwidth, increased performance and the isolating of the non relevant network traffic. Switches are very valuable network devices and they increase the speed and overall performance of a computer network.
It operates at the data link layer of the OSI model and it is used for the data communication and routing the packets in the network. A switch is like a hub and unlike hub it does not broadcast the data to all the computers in a network. A switch is an intelligent device like a router and it maintains a switching table that is based on the IP and MAC addresses of the LAN/WAN computers. Based on the source and destination IP addresses of the packets, a switch forwards the packets to its destination.
Ethernet switch stores the data packets and based on the source and destination IP addresses of the packets, it transfers the packets towards its destination. Switching table maps the Ethernet address and the switching ports through which the communication of these packets takes places. The implementation of the network switches is very common in the Ethernet. Ethernet switches supports 10 mbps to 100 mbps Ethernet standards. Splitting and forwarding the data packets splits the network into the collision domains and each network segments acts as an independent collision domain.
Different types of switches are used to connect different networks such as Ethernet and Fast Ethernet. To avoid the network congestion and to improve the performance it is recommended to add more switched ports in a network. A switch can connect a fast Ethernet to the existing Ethernet infrastructure to increase the speed and performance.
In the data communication networks, the combination of the Cisco Router and EtherSwitch modules increase the performance and bandwidth of the voice, video communications and the IP networks. The Cisco’s EtherSwitch module provides easy configurations, deployment and management in a single platform.
The key features of the EtherSwitch module includes Port auto sending, Qos, VLAN support and 802.1D spanning tree protocol. Adding the more switches in a non congested network can actually degrade the performance by delaying the network response time, packet switching delays, switch buffer delays and retransmission of the packets.
By using the appropriate network monitoring and troubleshooting tools, the better network performance can be achieved by load balancing, bandwidth monitoring, resources allocation, packet filtering and protocol analyzing. The combination of the fast Ethernet and the switched network overcome the bottleneck problem in the slow networks.
The most common switching features include the following.
Port Mirroring
• Turn the ports on and off
• Priority settings for Ports
• Link speed
• Duplexing
• MAC address filtering
• Use of Spanning Tree Protocol
• VLAN
• Network Address Control 802.1X
How to Build a Computer Network
A Simple Network
A simple computer network may be developed from two or more computers. Each computer will require a NIC card and a special cable known as a cross over cable. If the computers are more than two then a specialized networking device known as hub or switch will be required and all the computers in a network will be connected with the hub or switch. A simple network is useful for home networking. Additionally, a network between the two computers can be established by using a standard connection such as Rs-232 serial port on both computers connecting with each other by a special cross lined null modem cable.
Practical Networks
Practical networks generally consist of more than two computers and require specialized devices along with the NIC cards and these devices can be hubs, modems, switches, routers and others.
Common Types of Networks:
Following is the list of the common computer networking types.
LAN (Local Area Network):
A network that is limited to a relatively small geographical area such as a room, building, school network, ship, aircraft or a small office. LANs are also known as single location networks. The large LANs may be divided into the smaller logical segments known as workgroups.
CAN (Campus Area Network):
A network that connects two or more small LANs and is limited to a specific geographical area, such as a school, college, university campus or a military base, is known as a CAN. A CAN is generally confined to an area that is smaller than a Metropolitan area network.
MAN (Metropolitan Area Network):
A network that connects two or more LANs or CANs within a geographical area in a town, city or a metropolitan area is known as a MAN. A number or communication devices are required to create a MAN such as routers, switches, hubs and modems etc.
WAN (Wide Area Networks):
A WAN is a data communication network type that covers a very large geographical area. WAN networks can be privately owned such as a multi national company network or publically own such as internet. WAN technology generally functions at the lower three layers of the OSI model. Internet is the best example of WAN. There are two main types of WAN centralized and distributed WAN. The centralized WAN consists of a central computer that is connected to the dumb terminal or other types of the communication devices, such as a bank and post office networks. The distributed WAN consists of two or more computers that are physically placed at different locations and may also include connections to dumb terminal and other connecting devices.
Internetwork:
Two or more networks or connecting together using communication devices such as router. Any interconnection between private, commercial, public or government network may also be defined as internetwork. A specific internetwork consists of international interconnection of government, public and private networks.
Intranet:
An internetwork or a network that is limited to a single organization and uses TCP/IP protocol suite, HTTP, FTP and other protocols. Intranet can be categorized into LAN, MAN, CAN and WAN. Intranet is a company’s private network that is only accessible to the authorized users.
Extranet:
Extranet is a combination of intranet and some other trusted networks. For example a company’s customer may be provided access to the intranet, creating an intranet and while at the same time the customer may not be considered trusted with regards to the security of the company. An extranet can also be categorized into CAN, MAN and WAN and by definition extranet cannot be considered to consist of only a single LAN. An extranet must have at least one connection the extra network. Intranet and extranet may also have the connections to the internet. But only the authorized users can enter into the extranet internet plays a role only of a portal.
VLAN
A virtual LAN commonly known as VLAN is a method of creating independent logical networks within a physically network. Many Vlans can consist in a physical network. Vans help in reducing the broadcast domain and aids in network administration by separating the logical segments of a LAN. VLANS behaves as if connected to the same wire even though they may actually be physically connected to the different segments of a LAN. VLANs can be configured with software rather than hardware. One main advantage of the VLAN is that when computers are physically moved from one location to another, they can stay on the same VLAN without the reconfiguration of the hardware and software.
Computer Network Architectures
Basically computer network architectures are dividing into three basic types such as LAN (local area network), MAN (Metropolitan area network) and WAN (wide area network. A LAN can consist of two or more computers in the same room or building. Fiber optic or Ethernet cables are used to connect the computers in a LAN. Home networks, personal networks and office networks fall in LAN. A typical MAN consists of two or more computers at two different geographical locations in the same city.
A MAN can be wired (fiber optic cable) or wireless and a number of communication devices are used in a MAN. A WAN consists of two or more computers in two different geographical areas (different cities or countries) and there are different methods to connect the computers in a WAN such as leased lines (ISDN lines, radio waves, microwaves, dial-up connections and connectivity through satellite. The internet is a largest WAN in the world. With the invention of the wireless networking, mobile and optical technology the usage of the wires has been decreased. There are a number of the terms that describe the architecture of a network.
Computer Network Topologies
The topology or physical design is closely related to the architecture of a network. Topology defines that how the network is physically connected. There are three main types of the topologies.
• Star Topology: In the star topology the all the networking components are connected to the central point, which is a hub or a switch. The star topology is mostly in use in LAN.
• Bus Topology: In the Bush topology the networking components are connected to the same cable. This is also called linear bus or backbone.
• Ring Topology: In the ring topology the all the components are connected with each other in the form of a ring. A token continuously passes through the loop.
Network Architecture Terminology
• CAN (campus area network): CAN is a type of a network that connects the buildings/offices of a university, educational or office complex.
• Intranet: Intranet is a private network that belongs to an office, college or an organization and that is only accessible to the authorized users.
• Internet: The internet is a network of networks and connecting millions of computes with each other by different designs.
• MAN (metropolitan area network): MAN is a type of a network that is designed for a city. A MAN is larger than LAN but smaller than WAN.
• SAN (storage area network): SAN is a type of a network that is used to connect the storage related devices like RAID, file servers and tape systems.
• VLAN (virtual local area network): VLAN is a type of a network that allows computers on separate physical networks to communicate as if they were connected to the same network.
• Client-Server: Client- Server is a type of networking in which dedicated systems that provides services are called serves and the system that get these services are called work stations. The main services include file, printer, scanner, CD, Hard disk, processor, internet connection and other services.
• Peer-to-peer: This is a type of a networking where each computer shares the same functionalities. No centralized server is required in the Peer to peer networking.
Computer Network Protocols and the OSI Model
Protocol is one of the most important components of a computer network. Protocol means a set of rules, agreed upon ways or a communication language which all computer and devices understand. A protocol defines error checking, how data will be send and receive, and transmitting data between the systems. There are a large number of protocols and following is a list of the most commonly used protocol in the computer communications.
• AppleTalk: AppleTalk is a communication protocol that was developed by the Apple System to connect Macintosh computers to the printers.
• Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM): ATM is a type of protocol in which data travels in the form of fixed size packets. These fixed size packets provide high speed, data security, and video and voice communication over the same network.
• DECnet: DECnet is a protocol that was developed by the Digital Equipment Systems to connect the PDP and VAX systems.
• Ethernet: Ethernet is a LAN protocol that was developed by the Intel, Xerox and Digital Equipment System. Ethernet is a most widely used LAN communication standard.
• Fiber Distributed Data Interface (FDDI): FDDI is a protocol that is used to transmit the data over the fiber optic cables.
• Internet Protocols (IP): IP is a protocol transmitting data between the packet switched IP networks originally developed by the DOD (department of defense). TCP/IP (Transmission control protocol/Internet protocol) is a suite of protocol and FTP, HTTP, E-mail, Telnet are all IP protocols.
• Internetwork Packet Exchange (IPX): IPX is a networking protocol that is used by the Novell Netware operating systems.
• NetWare: Netware is a LAN protocol that is developed by the Novell Corporation.
• Signaling System 7 (SS7): SS7 is a telecommunication protocol that was developed by the International Telecommunication Union.
• Systems Network Architecture (SNA): SNA is a set of protocols that was developed by the IBM mainframe systems.
• Token Ring: Token Ring is a LAN protocol that was developed by the IBM where systems have the tokens before they transmit the data. Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP): TCP/IP is a suite of the protocols used to connect the computers on the internet. TCP/IP is a most commonly used protocol.
• X.25: X.25 is a protocol that was developed by CCITT for the packet switched network.
Protocols are combined with the OSI layers model. OSI model is an ISO standard for the communication system. There are seven layers in the OSI model and each layer performs the different functionalities. The seven layers are Application, Presentation, Session, Transport, Network, Data link and physical layers. Each layer know how to communication with the upper and lower layer. You can remember the name of all the layers by the following sentence.
Computer Networking Guide
Computer networking is a process of linking computers and devices with each other for data communication such as transferring files, videos, pictures and sharing network resources. A computer network is a series of points and nodes that are interconnected with each other. Computer networks can interact with other networks by two ways wired or wirelessly. The specific cables that are used in the networking are UTP (unshielded twisted pair), STP (shielded twisted pair), copper wire and fiber optic cables.
The two common networking systems are client/server and peer to peer. In client/server computing system, every client computer is dependant on the server for data sharing, logon access, printing and internet access. In case of server failure, the communication of all the client computers with the server is failed. In the peer to peer network, there is no centralized server and peer to peer model is suitable where security is not the main concern. Topology refers to the architecture, physical layout or design in which network devices are connected with each other. There are different topologies that are used in the client/server network communication system.
The most common topologies are BUS, STAR, RING, MESH and FDDI (Fiber Distributed Data Interface).
Network devices include router, NIC, modem, Hub, Switch, access points, wireless NIC and cables. Hub/Switch is a centralized LAN communication device and every computer in a network is directly connected with the Hub/Switch.
On the other hand a router is a LAN/WAN communication device and is used to connect two logically and physically different networks i.e. it connect two networks that operates on the different protocols TCP/IP and IPX/SPX and it connect the networks that has IP addresses of different classes.
Router is an intelligent device and its operating system has a pool of the IP addresses of the adjacent routers also known as next hopes. Every data packet contains the IP addresses of the source and destination routers and the data is routed towards the destination router based on its IP address. Router operating system is also known as Internetwork operating system.
With the broadband internet technology, voice, data and video can be shared at the same time. High speed wireless communication systems exist such as Wi-Fi and Wi Max to provide high speed and more bandwidth that supports multiple applications at the same time.
There are different communication protocols and TCP/IP is the most common LAN/WAN communication protocol. Protocol is a set of rules, agreed upon ways or standards that every device in a network supports to make the communication successful.
A computer network is categorized into the three types LAN, MAN and WAN.
Planning a Logical Network Design
When you plan a logical network design you can either start from scratch or upgrade an existing network. You should have the sufficient information about the networking components, hardware, protocols and topologies. You should analyze the traffic pattern, security needs, future expansion, and server capability, internet access to the clients, FTP and other things. You should also make a plan for the disaster recovery, data recovery and instant troubleshooting techniques.
An Overview of Computer Network Topology
Here you will learn network topology introduction, how computers get connected, bus, star, hub, hybrid, mesh, tree topologies and network physical design. In Computer Networking “topology” refers to the layout or design of the connected devices. Network Topologies can be physical or logical. In this section I will illustrate on the different types of the topologies.
Physical Topology means the physical design of a network including the devices, location and cable installation.
Logical Topology refers to the fact that how data actually transfers in a network as opposed to its design.
Topology can be considered as a virtual shape or structure of a network. This shape actually does not correspond to the actual physical design of the devices on the computer network. The computers on the home network can be arranged in a circle shape but it does not necessarily mean that it presents a ring topology.
Computer network topologies can be categorized in the following categories.
• bus
• star
• ring
• mesh
• Tree.
Hybrid networks are the complex networks, which can be built of two or more above mentioned topologies.
Bus Topology
Bus topology uses a common backbone to connect all the network devices in a network in a linear shape. A single cable functions as the shared communication medium for all the devices attached with this cable with an interface connector. The device, which wants to communicate send the broadcast message to all the devices attached with the shared cable but only the intended recipient actually accepts and process that message.
Ethernet bus topologies are easy to install and don’t require much cabling and only a main shared cable is used for network communication. 10Base-2 and 10BaseT are two popular types of the Ethernet cables used in the Bus topology. Also, Bus network works with very limited devices. Performance issues are likely to occur in the Bus topology if more than 12-15 computers are added in a Bus Network. Additionally, if the Backbone cable fails then all network becomes useless and no communication fails among all the computers. Unlike in the Star topology in which if one computer is detached from a network then there is not effect on the other computers in a network.
Ring Topology
In ring Network, every computer or devices has two adjacent neighbors for communication. In a ring network, all the communication messages travel in the same directory whether clockwise or anti clockwise. Any damage of the cable of any cable or device can result in the breakdown of the whole network. Ring topology now has become almost obsolete.
FDDI, SONET or Token Ring Technology can be used to implement Ring Technology. Ring topologies can be found in office, school or small buildings.
Star Topology
In the computer networking world the most commonly used topology in LAN is the star topology. Star topologies can be implemented in home, offices or even in a building. All the computers in the star topologies are connected to central devices like hub, switch or router. The functionality of all these devices is different. I have covered the detail of each networking devices in the separate portion of my website. Computers in a network are usually connected with the hub, switch or router with the Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) or Shielded Twisted Pair Cables.
As compared to the bus topology, a star network requires more devices & cables to complete anetwork. The failure of each node or cable in a star network, won’t take down the entire network
as compared to the Bus topology.
However if the central connecting devices such as hub, switch or router fails due to any reason,then ultimately all the network can come down or collapse.
Tree Topology
Tree topologies are comprised of the multiple star topologies on a bus. Tree topologies integrate multiple star topologies together onto a bus. Only the hub devices can connect directly with the tree bus and each Hub functions as a root of a tree of the network devices. This bus/star/hybrid combination supports future expandability of the computer networks, much better than a bus or star.
Mesh Topology
Mesh topology work on the concept of routes. In Mesh topology, message sent to the destination can take any possible shortest, easiest route to reach its destination. In the previous topologies star and bus, messages are usually broadcasted to every computer, especially in bus topology. Similarly in the Ring topology message can travel in only one direction i.e clockwise or anticlockwise. Internet employs the Mesh topology and the message finds its route for its destination. Router works in find the routes for the messages and in reaching them to their destinations.The topology in which every devices connects to every other device is called a full Mesh topology unlike in the partial mesh in which every device is indirectly connected to the other devices.
TYPES OF TOPOLOGY
Linear Bus
Ethernet and local talk networks use linear bus topology. In Linear Bus topology, each device is directly connected to the linear cable.
Star
In the star topology each node such as computers, file server, workstations and peripheral devices are directly connected to the centralized device known as hub or switch. Data in the star topology passes through the hub or switch before it reaches to the destination. Hub or concentrators also act as repeaters for the data flow. Twisted pair cable, coaxial cable, and fiber optic cables can be used. Star wired topology appears to the same as star topology. The Token Ring protocol uses star-wired ring topology.
Tree
Tree topology is the combination of the linear bus and star topology. Linear Bus consists of the star configured workstations connected to the Linear Bus backbone cable.
Token Ring
Token Ring was developed by several manufactures and it is used for high traffic network loadings. Ethernet now has taken the popularity of the Token Rings.
Networking Hardware
Numerous types of the computer networking hardware is used develop a computer network such as Routers, hubs, workstations, NIC cards, servers, firewall, switches, bridges, modems, local talk connectors, UTP/STP cables and many other types of basic and advance communication hardware.
Summary
Topologies are the important part of the network design theory. A better network can be built if you have the knowledge of these topologies and if you know the difference between each topology. Similarly you should have the knowledge of each network device so that you can properly use them according to your network needs. A misconfigured network can result in a waste of time and energy as well as a lots of troubleshooting methods to resolve the issue. So thebasic understanding of the network topologies and network devices is a must to build a good network.
Components of a Network
Different types of physical components are involved that builds a LAN/WAN computer network. The major components are hubs, NIC adapters, network cables, routers, switches, modems and gateway. Following is the basic overview of each of the major component of a computer network.
Servers :
Network servers are computers that provide different services to a computer network such as logon authentication, internet access, disk space, printing access, CD/DVD-ROM access, database access, antivirus and other software application updation etc. The specialized server operating systems are Windows 2000 Serve, Windows 2003 Server, Linux and Sun Solaris. In the Windows 2000/2003 server, active directory holds the users and network computer information
INTRODUCTION TO NETWORK SERVERS
Here you will learn the basic types of network servers such as proxy server, web server, database sever, file server and print server etc. A server is a dedicated computer that is designed to perform additional tasks for itself and for other client computers in a network. Network servers and specifically designed to perform extra tasks and process the simultaneous requests from the client computers.
A server computer is normally equipped with the extra hardware such as external memory, hard disk and processor. A server can perform many tasks simultaneously and process different types of requests such as logon requests, files storage, print requests, internet access and many other requests. There are many types of the servers that perform different tasks such as handline file requests, logon requests, internet access, time management and synchronization, fax services and network storage services.
FILE SERVER: A file server is a dedicated computer in a network that is used to store the files such as word processing documents, spreadsheets, financial data and other useful information. Typically a file server has a large memory and additional hard disks. Server itself and all the client computers stores data on the file server and access it again when required. Additionally, file server software such as Windows 2000 Server, Windows 2003 Server also acts as the logon server and process the logon requests of the client computers.
PRINT SERVER: A print server is a network computer or a specifically designed device to which print devices or printers are attached. A network print server is used to serve the client’s printing requests from all over the network. A Windows 2000 or Windows 2003 computer can serve as a print server. The client computers connect with the print server by using Microsoft Network Printing Protocol.
PROXY SERVER: A network proxy server is an intermediate computer between the client computers in a network and the internet. A proxy server forwards the client’s requests for the specific web pages to the web server. A proxy server when receive the response from the web server (in the form of web pages) it stores a copy of every web page in its cache. So that if next time another client request for the same web page it won’t go to web server for this page, instead it will return the web request from its own cache. A proxy server is software program and when installed on a computer, the computer acts as a proxy server. The most commonly used proxy server programs are WinGate, Win Proxy, and Microsoft ISA Server etc.
Introduction to Firewall
A network firewall is a group of systems that is used to control the access between two different local and remote networks. Firewall protects the networked computers from intruders, hackers and unauthorized users that can compromise the security and privacy of your computer. Firewall selection and implementation in a network cab be a time consuming process. Network firewalls provide barriers and denies any unwanted internal and external traffic. A firewall can be software that is installed on a host system, a router, network appliances that are designed to provide the firewall services.
A personal computer or a gateway computer without firewall implementations can be attacked by intruders and hackers. By segmenting a physical network into sub networks, firewall reduces the damage that can be spread to the different sub networks.
Types of Firewall Systems
Following are the three main types of the firewall.
1. Packet Filtering
2. Proxy Server
3. Application Gateway
In Packet filtering mechanism, untrusted packets are blocked and only trusted packets can be transmitted in the network communication. This type of filtering provides limited functionality because you can’t get the origin of the traffic, time and sizes of the files that are transmitted.
Packet filtering works at the network layer of the OSI model and makes the logical decisions based on the IP addresses of the source and destination. In the client/server network model proxy server provides the indirect access to the internet because all the incoming and outgoing traffic is monitored and filtered at the proxy server.
In this system, detailed information about the two way traffic can be gathered. Application gateway provides the highest level of security, performance and scalability.
What is a Proxy Server?
A proxy server is a computer that offers network and internet access services to the client computers in a network. A client computer connects to the proxy server, requests a connection, services, files and other resources on the other servers. In some cases, the proxy may alter the client’s request and the server’s response for various reasons. By using the proxy server you can hide, conceal and make your network id anonymous by hiding your IP address. To get the anonymous status on the network or Internet, strong intermediate methods are employed like cryptography etc. Examples are remailers, P2P systems etc.
There is a large number of the software available that allows you to hide your IP address with the help of the proxy servers. The well known software for this purpose is Hide IP, Stealth surf, Netconceal, Anonymous surfing, Proxify and Ghost surf.
An IP address is a unique identification number for communication between computer networks, network devices such as computers, fax machines, printers and servers. It is like the number of an apartment or a phone number. IP addresses are of two types Static and Dynamic. Internet service providers’ use dynamic IP addresses and servers usually use static IP address.
The class A of the IP address constitutes almost 50% of all the IP addresses. This class is meant for large networks like the big multinational companies. Class B networks are medium sized like used in the colleges, Universities and other educational and training institutes. Class C IP addresses are usually used for the small companies.
The Regional Internet Registry (RIP) provides the IP addresses based on the geographical distribution. RIP also offers protection against the hackers that try to access the confidential data. All the personal information recorded by the ISP is kept in confidentiality.
How Firewall Works
The firewall stays in the background and monitors incoming and outgoing traffic. It stays between the junction points between the two networks usually a private and public network.
Firewall works on the access and denial methods. It may allow all traffic if it meets the criteria or it denies all traffic if it doesn’t meet the criteria set in the firewall applications or hardware appliances. Firewall criteria is concerned with the source of the traffic, IP addresses, ports no and the type of traffic.
There are certain rules that can be implemented to put security check on the traffic. By implementing firewall on your home or network computer you can protect yourself potential security threats on the internet such as identity theft, privacy lost, data lost and attacks from hackers. Firewall can hide your internet-connected computers and block ports.
Implementation Requirements
There are many important components and configurations are involved in the firewall implementations. Many network administrators configure rules and filters without testing them. The best practice is to install the firewall solution in a test environment. Testing may involve scanning all the open ports from internal trusted and outer untrusted network.
Closely check the log files and ensure that the firewall is tracking the things that were specified. Run each test again and again.
Introduction to Firewall
A firewall is considered as a first line of defense against the unauthorized access, internet hackers and internal and external security threats. A firewall is a software or hardware and it is usually installed and attached with the gateway computer that sits between the private computer and the public computer. The basic purpose of the firewall is to block the unauthorized access and filter the internet traffic. Once installed, firewall sits in the background and monitors all the incoming and outgoing traffic. Firewall software provides the convenient interfaces and other features to define the custom rules. Firewall secures company’s internal network from the unauthorized external access in the form of internet hackers.
Firewall is implemented in the LAN, MAN, WAN and wireless network. A firewall is specifically installed on the designated computer known as gateway. Different companies use different firewall products and the main features include logging, reporting, filtering, blocking and monitoring. The most common firewall techniques are packet filtering, network address translation, application gateway, proxy server and circuit level gateway
Network Firewall
A network firewall can be implemented in a variety of ways. Firewall selection and implementation can be a time consuming process. Organizations with a connection to the internet or any other untrusted network must implement a trustworthy firewall solution for blocking the unauthorized access. A firewall can be consist of a router, multilayer router, single computer, multiple computer running firewall software and hardware to provide the firewall functionalities.
The major functionalities of the firewall as mentioned above are the user authentication, logging, monitoring incoming/outgoing traffic and reporting. Along with the positive features of the firewall there are some negative features and that includes the traffic bottleneck in network computing, single point of failure, increased management and customized configurations for the different network applications, network computers and users. Most network firewall software uses the preconfigured rules to filter out the incoming and outgoing traffic.
The well known methods on which firewall software works are packet filtering, stateful packet inspection and applications gateway/proxies. Hybrid packet filtering is used to combine two or more firewall methods to provide the additional security. The packet filtering rules allow or deny the traffic based on the IP addresses of the source and destination, protocol type, source and destination ports of the network devices. Packet filtering works at the lower level of the OSI model and it gives minimal impact on the overall network performance.
Top Network Firewall Software
Following list provides the detailed review of the well known and standardized firewall software.
• Zone Alarm
Zone alarm is a well known firewall software and it provides protection against the hackers, data theft, pop ups, viruses and other security breaches on the internet.
• Outpost Firewall Pro
Outpost firewall pro provides protection against the unauthorized access, intruders, spyware, network attacks and malicious software.
• Norton Personal Firewall
Norton Personal Firewall software is well known firewall software. The key features are filtering the outgoing and incoming internet traffic, defense against viruses, Trojan horses, viruses, pop ups and other internet threats.
• McAfee Personal Firewall Pro
McAfee Personal Firewall Pro is award winning software that defends your business against the unauthorized access, viruses, hackers and internet spasm.
• Bull Guard
Bull Guard Internet security 7.0 has all the security features, which your computer requires. The main features includes spam filter, firewall, anti spyware, antivirus and all in one security features.
• Sygate Personal Firewall
Sygate Personal Firewall provides multilayer security for the network, operating system, content, applications and internet access. The advanced features provide protection against the intruders, Trojan horses and DOS attacks.
• Panda Platinum Internet Security
Panda Platinum Internet Security protects your confidential information and keeps the hackers out. The key features include antivirus, anti spyware, anti phishing, firewall, identity protect, backup, anti spam and parental control.
WEB SERVER: A web server is a computer that is used to respond the client’s HTTP requests (usually web browsers) and return the response in the form of the web pages, images, voice files, graphics, video clips and others. A single web server is capable to host many websites. Web servers also host shared web based applications and a large number of clients access them simultaneously. Some applications on the web server require some authentication methods such as login name and password. Some dynamics content and applications host on the web server used some related interfaces such as JSP, ASP, PHP, CGI and .NET. HTTPS is used to establish a secure connection between the client and the web server and it is normally used during the credit cards transactions, online shopping where high security is required. A web server is also known as a virtual host when it hosts a large number of the websites on the same IP address.
DATABASE SERVER: There are many database server programs such as Oracle, MySql, and Microsoft Sql 2000. A database server program is used to process the database services. In a client/server networking model, the server component of the database servers (Oracle, MYSQL, and SQL2000) is installed on the server computer and client component of the database program is installed on the client computers in a network. Network distributed applications use database at the backend, which is usually installed on the server computer. In network computing, a database computer should be configured separately and in the enterprise network a large number of the database computers are used, which synchronized with each other.
VIDEO SERVER: A Video server is an online storage computer that is used to provide the video and voice access to the network clients. A video server is used in the broadcast industry, entertainment and in news. A video server also provides online course and lectures to the registered users from all over the world.
STORAGE SERVER: A storage server is high quality and high speed storage device or a computer that is used to store the data of the network applications that are running on the other computers in a network.
TIME SERVER: A time server is a multipurpose, dedicated network computer that is used to compare the time from the atomic clocks and distribute the time among the other network computers. A file server can become a time server by using the NTP (Network time protocol). A NTP is used to synchronizing and distributing the time in a network.
ACCESS SERVER: Access server or Remote Access server is a network device or a computer that is used to access the network by a larger number of the network users. ISP mostly has RAS servers configured and access by a large number of the users.
FAX SERVER: A fax server is software program and when it is installed on a file server, it acts as a Fax server. A fax server is usually a dedicated server attached with a dedicated fax device, fax modem and a telephone line. The fax software receives the fax and converts in the fax form. In the big networks, a fax server can be used as a dedicated computer. There are many only fax services providers like efax.com and upon subscribing to them you can send fax all over the world with a low cost fees.
What is a Web Server?
Learn Web server software overview, how to configure, how it works, apache, tomcat. Web server is a computer including a software package that provides the specific services to the client computers. Web server delivers the web pages. Every web server has an IP address and a domain name. If you sends a request through your browser for this website http://www.networktutorials.info, the request goes to the server whose domain name is networktutorials.info.
The server fetches the index or main page of the website and sends it to your browser. Web-based servers are used for hosting the websites. One web server can hosts thousands for one sites. But in the hosting companies there are number of the web servers for load balancing and sharing the other services.
The web hosting companies offer different types of hostings services including Ecommerce hosting, CPanel hosting, PHP hosting and reseller hosting.
A computer can be act as a web server by installing and configuring the server software and connecting the computer to the Internet. Normally, web server computers have to be turn on (online) for almost all the day.
There are many software applications that are used as the web server like IIS, Apache web server, Tom Cat web server. A web server typically accepts thousands of the concurrent incoming requests for the specific domain, that it hosts.
In case if the server is down for any reason, the websites that are hosted on this server cannot be accessed. So the downtime is a biggest negative thing for the web hosting companies. Many hosting companies have to mention the uptime of their servers for the client’s satisfactions like 99.9 % uptime. You may have seen this percentage on many hosting companies’ websites.
The web servers serves the objects in the form of html documents, plain text, images, sounds, video and some other form of the data. Many of the data types may not be placed in the static form but they are shown on the run time by the software programs, that are installed on the web server and the CGI scripts are the most common form of these programs.
Web servers and the browsers such as internet explorer, Firefox, Netscape, Opera etc communicate with the web server by using the HTTP protocols (Hypertext Transfer Protocol). This is very effective method of requesting the data over the Internet. Web servers are in various shapes and sized and run under different operating systems like Windows, Linux, and Unix etc. They are also range differently in prices and working.
Apache Web Server
The Apache web server is the most popular and most commonly used web server today. Apache web server has many features and good functionality that appeals to the users and that’s major cause of its popularity. On the other end, Microsoft’s IIS still is struggling to complete fully with apache web server. IIS is a very good server on the NT platforms and Apache is compatible with the Linux/Unix platforms.
Another big reason for the worldwide acceptance of the Apache web server is its stability. Many big websites on the Internet has chosen Apache web server for their hosting needs.
Additionally, Apache web server is a relatively fast. If your website contents are static then Apache’s working is very efficient and fast and on the other end, if you are using scripts like CGI scripts or others, it usually slows down the speed of the Apache web server.
A Web server is simply a little piece of the software, it takes the file name sent in the GET command, retrieves that files and send it back to the browser.
Most servers implement some level of security on the serving process. For example login/password accessible page requires the proper login and password from the users to accept that page. Web servers have the database and login information of the entire subscriber and only a subscriber of that typical service will be able to see that page. Additionally, while doing secure transactions the web pages allows encrypted transactions between the browsers and the servers such as on the E-commerce websites and other websites where a transaction through a credit card is required.
Basic Overview How Web Server Works
A web server performs various tasks on the request from the clients. To understand the working of the web server, it is necessary to first understand that what is client and server and what is their relationship with each other. A client is a program that sends request to a server and server responds to the requests of the clients.
This generic definition covers many types of relationships between client and servers like database server & web server etc. Web server have to be connected to the internet because client computers need to access them for various needs like data, files, graphics, video and html documents access.
The client program such as browsers and typically designed for the purpose of communicating with the web servers. A browser itself has different levels of features and security. To start the communication between the client (browser) and the server, a set of rules or agreed upon way is required and that is called a protocol. To access the web pages from the server HTTP protocol is required and for the file sharing access FTP protocol is required. There are a large number of the web protocols.
A web server is configured and designed in such a way that it responds to the thousands of the concurrent incoming requests from the clients for different things like html documents, graphics, images or video etc.
Cabling
There are different types of network cables are involved in a compute network such as coaxial cable, Ethernet cable UTP/STP and fiber optic cable. The most commonly used cable in a local area network is UTP/STP (Unshielded twisted pair/shielded twisted pair). However fiber optic is currently replacing all the traditional cables and is being widely used in LAN and WAN networks. Data travels at the speed of light through the fiber optic cables thus fiber optic is a fastest data carrier in the computer networks.
LAN cards
LAN cards, NIC or network adapters are the essential physical parts of any computer network. Every computer in a network requires a LAN card to get connected with the other computers in the network. Every LAN card is assigned a unique IP address for computer’s identification on the network. Wireless LAN cards are used in the wireless LAN.
Switch/Hub
Hub or switch is a centralized device and both devices almost play the same function i.e. every computer in a network (in star and mesh topology) is directly connected with the hub or switch. The major difference in hub and switch is that when data arrives at hub it broadcasts it to the every the computer in a network and only the destined computer accept the data however the in case of switch, data is only transferred to the destined computer and not to the all computers. Switch provides more data transfer speed as compared to the hub. In the advanced switches, a switching table is maintained, which has the database of IP addresses and MAC address of every computer.
Router
The basic function of the router is to route the traffic (data) to its destination based on the IP address. Router is a most important network communication device in LAN and especially in WAN and the whole communication system of the internet is based on the routers. Router is a key component is WAN. Like in the advance switches, Router maintains the routing table, which contains the IP address of the source and destination routers. With the help of the routing table, a route finds the best shortest possible path of the destination. Routing tables are continually updated and this updatation is propagated in all the connected routers.
Antenna
Antennas are the part of a wireless computer network for boosting the signals for adapters, access points, and bridge equipments. Antennas also provide the building to building wireless connectivity and some of the types of antennas are directional antenna, video antennas, yagi antennas, wireless communication antennas, omni-directional antennas, and base station antennas.
Modems
Modem is a network device that performs two functions modulation and demodulation i.e. it converts the digital data into the analog signals and the analog data into digital.
Gateway
A network gateway is a computer, software or device that is directly connected with the external network i.e. internet. All the incoming and outgoing traffic of a network passes through the gateway. Gateway computers are kept very secure as the can be attacked directly through the internet and in case of any security holes and weaknesses in the gateway computer, all the computers in a network can be attacked.
Backbone
A backbone is a main line of wire such as fiber optic cable that connects two or more big networks such as ISPs.
Introduction to Network Cables
Communication is the process of transferring signals from one point to anotfher and there must be some medium to transfer those signals. In computer networking and especially in the local area networking, there are certain communication mediums. This section provides the basic overview of the network cables, lan communication system and other transmission mediums in LAN and WAN. Today many standardized communication cables and communication devices are in use the according to the needs of a computer network. LAN data communication systems there are different types of cables are used.
The most common types of the LAN cables are the Ethernet UTP/STP cables. An Ethernet cable is a twisted pair cable that is consist of eight cables that are paired together to make four pairs.
A RJ-45 connector is joined with both ends of the cables and one end of the connector is connected with the LAN card of the computer and the other end of the cable is connected with the hub or switch. Cable testers are used to test the performance of each cable. The preferable cable in the Ethernet networking is the 100baseT, which provides the best communication speed. UTP/STP is a standardize cable in which data is transferred which provides the transmission speed of 10/100 mbps.
The most commonly used cable in the star topology is the UTP/STP cable. UTP/STP cables are same in functionality only a slight difference is that an extra protective silver coated layer surrounds the cable. UPT/STP cables are further divided into straight over and cross over cables. The most common use of the UTP/STP cables is the serial transmission, Ethernet, ISDN, fixed and modular interfaces in the WAN networking. Straight over cables are used to connect the computer with the hub or switch and a cross over cable is used to connect the hub with a hub or with a switch.
In the cross over cables, first and third cables and crossed with the second and sixth cable. There is another type of the cable which is coaxial cable that is used in the bus topology. All the computers in the bus topology are connected with the same coaxial cable thus forms the shape of a linear bus. If any portion of the cable is damaged, then the whole cable becomes useless. Another common use of the coaxial cable is in the cable TV network. An outer protective covering provides insulation between the inner copper wire and the outer twisted metal field.
Coaxial cables are also used in the microwave frequencies but there not as popular as other cables. The most advanced form of the communication cables is the fiber optic cable. Fiber optic cable is a very expensive cable that is composed of a number of thin fibers that are covered with the insulating covering. Data is traveled at the speed of light in those fibers. Today FTTH (fiber to home installation) is becoming very popular and FTTH is giving the speed of 100 mbps to the home users. According to the current trend of the home networking and bandwidth requirements, fiber optic cable will replace all the other cables. Once the price of the fiber optic cables is reduced it will be more in demand for every home and office network.
Fiber optic cables are designed for high speed data communication for the corporate offices and ISPs, backbones and in the telecommunication industry. Fiber optic cable acts as a backbone cable when it connects two ISPs with each other. In the internet communication, there is a major role of the fiber optic cable, which acts as a backbone. There is another type of cable which is called Roll over cable that is used connect the consoles of the Cisco Routers and switches and RJ-45 connectors are used to at the both ends of the roll over cables. Today many networks are shifting to the other types of the networks such as radio transmission, infrared; Bluetooth and these all are the type of the wireless networking. Wireless networking has its own infrastructure where access points, routers, switches, wireless network connections and wireless network cards are used. The only major difference in the wireless and wired networking is the usage of the cables, which plays the role as a transmission medium.
Introduction to the Network Communication Devices
In this tutorial you will learn get the basic introduction to network devices such as nic adapters, routers, hubs, switches, modems, communication cables, lan/wan routers, gateway and other devices. A network is consists of a larger number of the communication devices. The simplest device that is used in the communication is the NIC adapter which is attached with the every computer in a network. If you want to build a LAN, you will need to have computers, hubs, switches, network adapters, UTP/STP cables, routers, internal/external modems, connectors, cable testers and clipping tool.
On the other hand if you need to build WAN, you will need to have routers, switches, dedicated or leased telephone lines such as ISDN lines, frame relay connection and other types of wan communication connections.
There are different communication mediums such as Ethernet cables, copper wire, coaxial cable, fiber optic cables, leased telephone lines and ever air is also a communication medium for the satellite communication. The most common networking medium is the LAN is the Ethernet cable (UTP/STP), which is used in the star topology. Hub is a central device of a network and every computer in a network is directly connected with the hub.
If the hub fails to work, the communication between the computers stops till the hub again starts working. Hub broadcasts the data to its every port, and then finding the destined computer, the data sent toward it. The switch is an advance form of the hub similar in functions but the advanced switches has a switching table in them. A advanced switch stores the MAC address of every attached computer and the data is only sent to the destined computer, unlike the hubs where data is sent to all ports. A router is a key device in the internet communication and wan communication system. A router has software called routing table and the source and destination addresses are stored in the routing table.
A router connects two logically and physically different networks. Router finds the IP address of the next hop (next router) and the data is sent toward it and so on. The well known routers developing companies are Cisco systems, Nortel, DLink and others. Every ISP, banks, corporate offices and multinational companies use routers for LAN and WAN communications and communication in their private networks. A gateway can be device or software in a network.
A gateway device connects the LAN with the internet. A gateway is directly exposed to the internet so it should be securely configured and in and out traffic should be monitored. If you are using DSL connection, you must need a DSL modem in your network. The telephone line is connected with the DSL modem and UTP/STP cable attaches your computer with the DSL modem. Modems are the devices that are used to modulate and demodulate the data. They convert analogue signals to digital and digital signals to analogue so that signals can travel on the telephone lines.
There are certain types of the cables that are used to connect two or more computers in a network. Fiber optic cable acts as a backbone between the ISPs and corporate offices. Data travels at the speed of light on the fiber optic cables. The cost and the installation cost of the fiber optic cable is very high but it is becoming very popular in the home networking and LANs also. In the local area networking, 10baseT/CAT5 cable is most commonly in use.
A server is a computer in network that provides services to the client computers such as logon requests processing, files access and storage, internet access, printing access and many other types of services. Servers are mostly equipped with extra hardware such as plenty of external memory (RAM), more data store capacity (hard disks), high processing speed and other features.
What is a Optical Network?
In this general optical network tutorial you will find basic overview of the fiber optic technology, communication glossary, lan/wan cables, communication devices and the fiber optic industry trends.. Optical network is a network of the fiber optics cables in which data travels on the thin fibers at the speed of the light. Today, many ISPs, corporate offices, LANS and even home networks are connected through the fiber optics though it’s still very costly but it provides a high bandwidth and data transfer capacity. Fiber optic cables act as a backbone when they connect different ISPs with each other and in case of any breakdown or any kind of problem in the backbone results in a communication failure at very large scale. There are a large number of the fiber optic cables are involved in making the whole internet.
Fiber Optic Technology
Fiber optic technology is most popular in the telecommunication industries as well as Local Area networks. Fiber optic cable is a bundle of various cables which are thin and provides a large bandwidth. The cost of the fiber optic cables is much higher and same is the installation of the fiber optic cables. Today, a large number of the communication networks depend on the fiber optics. Fiber optics is less susceptible to the outer interference than the metal cables. CCTV network, long distance switches, central offices, subscriber’s loop careers and industrial networks use fiber optics for communication purposes. In the near future, fiber optical cables will repalce the conventional coaxial and ethernet cables for the LAN networking.
Enterprise Optical Network.
Fiber optics also provides solutions for the enterprise networking like NAS (network attached storage) and SAN (storage area network). A NAS is a server that is used to data sharing in a network. NAS allows more hard disk storage space to be added to a network. A NAS device does not require to be attached to the server directly and it can be placed anywhere in the network. A NAS can be made up of two or more NAS and being a part of a network, the network user can access it from anywhere in the LAN. NAS is an efficient way of storage and file sharing. Fiber optics provide more efficiency and reliability in the NAS performance by providing more bandwidth and data capacity. SAN is a subnet of the shared storage devices in a LAN or a WAN. Fiber optics provide more high speed connectivity and speed among the SAN in a LAN or WAN.
Optical Network Devices
Fiber optic devices are in use in a number of ways like Networking, storage, industrial, medical, defense, broadcasting, telecommunication systems.
Optical testers are designed for a variety of measurements and tests with a single meter.
Attenuators are designed for single mode applications, multimode applications and for attenuation settings.
Fiber Optic connectors are used to connect a fiber with another fiber or equipment. There are different types of connectors are being used today such as SMA, FC and SC connectors.
Optical Switch is a handheld device for calibration sets and measurements automation.
Optical Routers connects twisted pair LONWORK notes to the fiber optic backbones or subnets. They also re-routes the data automatically due to power failure of fiber break.
Major Optical Network Terms
Adaptor: It is a device for connecting two or connectors.
ADSL: Asymmetric Digital Subscriber lines is a most common form of the DSL
Amplifier: It is a device that is used to amplify the signals without destroying the original wave shapes.
ATM: An abbreviation for the asynchronous transfer mode.
Attenuation: The reduction of the optical power as it passes through the fiber optic.
Attenuation: A device that is used to reduce the signal power in a fiber optic.
Backbone: Backbone is a high speed telecommunication network.
Bandwidth: The capacity of the medium.
Base band: A simplest method of the transmission in the LANS.
Biconic Connector: A type of the fiber optic connector.
Bit: An electrical pulse that carry signals.
Bandwidth: Capability of dealing with high speed, high capacity data transmission.
Cable: One or more fibers enclosed in the protecting covering.
CATV: An abbreviation of the community Antenna television of cable TV.
Coax: An abbreviation of the coaxial cable.
COMSAT: Communication satellite.
Coupler: A device that is used to distribute the power between two or more ports.
CWDM: Course wavelength division multiplexing.
Detector: Converts fiber signals into the electrical signals.
Duplex: The simultaneous operations of a circuit in both directions in a communication network.
FDDN: Fiber data distribution network.
Fiber optic modems: Used for sending and receiving data.
Fiber Storage: High speed network technology used for storage.
MT Connector: Multi fiber connector used to hold 24 fibers.
ODS: Optical data storage.
PHY: Known as physical layer device.
POF: Plastic optical fiber.
Port: Connection point.
PTO: Public telecommunication operators.
RFI: Radio frequency interface.
SONET: Synchronous optical network.
TDM: Time division multiplexing.
Trunk: Circuit that connects two switching centers.
X Band: Frequency ranges between 8.0 to 8.4 GHz.
Basic Introduction
• STEP 1: Router: A router relays the data between your computers and your internet connection.
• STEP 2: Network Adapter: A Network Adapter or NIC card is connected to each computer and it is used to send the data to each every computer and the router.
STEP 3: IP Address (Internet Protocol) is your computer’s unique identification on the computer network and over the internet. In your home network and a small network of a company all the computers share the same IP address over the internet.
• STEP 4: Print Server A print server is a specialized network adapter that is used to connect the printer machine to a network and with the print server several computers in a network share the same printer or print device.
How to Choose a Right Network Type
• STEP 1: Connecting your computer wirelessly over the radio waves is carried out by a specialized router called an access point. One access point is enough for networking an averaged sized home. The trade name of this technology is Wi-Fi or 802.11b. One important thing is that all the Wi-Fi products should be compatible with each other. Wireless communication is important for the people who go from room to room with their wireless laptops or they want to use their laptops in airports, hotels, cafes and other places where wireless service is available.
• STEP 2: Next you use your home’s wiring to connect the router to each computer with a powerline network. HomePlug is the trade name of this technology. It is seen that HomePlug networks are more secure than the Wi-Fi. But as compared to the Wi-Fi it is a new technology and is more expensive than Wi-Fi technology.
• STEP 3: Hook up with the Ethernet 10-Base-T or 100-Base-7. Ethernet is the best choice if your router, broadband internet connection and all the computers all in one room. Due to the cabling, involved in the Ethernet, it’s less flexible than the others.
Buying Equipment Instructions
• STEP 1: First of all get one router and if you want to go wireless this router will called an access point.
• STEP 2: Next get compatible NIC cards for each computer and plug them into the computer’s universal serial bus (USB
• STEP 3: If you are using a wired network the purchased extra long CAT 5 Ethernet cables.
• STEP 4: Next buy a print server if you want to put a printer in your home.
One important thing to note is that all the hardware should be compatible with each other.
Setup Instructions
• STEP 1: First of all read the manuals of the devices and start experimenting. Many products have good manuals and online support. You can easily get answers of the basic and advance questions. Many manufacturers provide online help and advice so there is no need to worry about any kind of technical support. Good technical support can save your lot of time and efforts. So before starting make a thorough plan to work on it.
• STEP 2: If you are planning to install a wired Ethernet, then run the cables to your home theaters or stereo. Now many new digital home products like digital video recorders and game systems are having the internet capability.
General Tips
In summary you should look for these things for installing a home network such as Router or access point, Ethernet cables, NIC adapter, Print Server and the technical support from the vendor or a useful website or forum on the internet. Hybrid networks have many advantages and so they are very popular. For example, you can have Ethernet going to a desktop computer and printer in your home office and additionally wireless router or access point for a roaming laptop and desktop computer in your bedroom.
Some cordless phones and the microwave ovens can interfere with a wireless communication. If you have any interference problems then move the access point and router and place them at some different positions.
It is very important that when you setup your router for the first time at your home, change its password because every hacker on the internet can know the default password of a router. Additionally, while making the wireless connectivity you must enalbe the WEP to keep the information private and secure from the hackers.
Additionally, install some anti spyware, good anti virus software on your server and client machines in your computer network and regulary update Windows operating sytem through the Microsoft's website.
Computer Network Tutorial
Networking Introduction
In this basic network tutorial you will find basic introduction to data communication and general overview of the communication devices, tcp/ip suite, communication cabling, basic topologies, and wireless communication technology. Computer networking means sharing of data and resources between two or more computers with a medium such as Ethernet cable, leased lines, router and even air. Networking is a most widely used field of the computer technology. A computer network is comprised of two or more wired or wireless connected computers. A simple computer network is made up of two connected computers. All the computers in a network can access, share the data and resources with each other. A computer network is generally categorized into the three main types such as LAN (Local area network), MAN (Metropolitan area network) and WAN (Wide area network). A number of the standards are involved into the certain steps of the data communication and on these standards certain communication devices have been developed.
In the computer age, no organization can work perfectly without a computer network. The concept and working of the whole internet is due to the computer networking. A computer network is a basic need for any organization to share data and resources on the small to big level such as banks, insurance companies, universities, colleges, multinational companies, corporate offices and small businesses etc. The network is made up of different components, protocols, devices, topologies and mediums such as cables, routers, leased lines and air. Following is the basic overview of each of the basic networking components.
TCP/IP Suite
TCP/IP is a suite of the protocols. Many protocols are the part of this protocols suite such as TCP (transmission control protocol), IP (internet protocol), FTP (File transfer protocol), HTTP (hyper text transfer protocol), DNS (Domain name service), DHCP (Dynamic host configuration protocols), PPTP (Point to point tunneling protocol) and many other communication protocols. The communication on the internet is carried out by the TCP and IP protocol. In LAN and WAN networking TCP/IP protocols play major role in the communication. An IP protocol ensures the error free delivery of the data to its destination by a device known as router.
Additionally, every communication device on the internet and on the local network requires a unique identifier, which is known as a IP address. An IP address is 32 bits, four octets address that is having a decimal value from 0 to 255. There are three major classes of the IP address such as Class A, Class B and Class C. A typical IP address looks like this form 100.100.1.50 that is four octets that are separated by the periods.
Topologies
Topology means the physical design and layout of the network or how the network devices, computers and components are arranged. There are some basic topologies of a computer network such as star, mesh, ring, bus, hybrid and tree. The most commonly used topology of a computer network is a star topology. In the star topology, all the computers are connected to a central device known as a hub or switch. Data in a network passes through the central devices and then directed towards the destination computers. The failure of one computer does not affect the working of the other computers however, the failure of the hub or switch results in halting all the network communication i.e no communication can occur without the hub or switch.
Network Devices
There are a large number of devices that are involved in the whole communication process. These devices include hub, switch, router, gateway and NIC cards. These communication devices play an important role in the overall data communication process. The communication on the internet is carried out by a device known as a Router. The main function of the router is to route the data (traffic) to its destination. Router has the IP addresses of the sending and receiving computers also router has the capability of finding the best shortest path to the destination and hence provides the faster secure delivery of the data. Different communication devices with different features are being developed by a large number of the vendors such Cisco, Intel, Nortel, DLink, Paradyne, Dell, 3COM, Alcatel, Fibronics, Triticom, Nextgen, Motorola and many others.
Cabling
A computer network can be formed wireless or cabled. In a cabled network, there are a certain types of the cables required depending on the type of the network. The most commonly used cables are the UTP/STP (unshielded twisted pair/shielded twisted pair) Ethernet cables also known as CAT5 cables. In the CAT5 cables, there are eight cables and four pairs. Each cable is twisted with its corresponding cable and thus forms a pair. From these eight cables, there are two major types of cables are formed known as straight over cable and cross over cable. A straight over cable is used to connect a computer with a hub or switch and a cross over cable is used to connect the computers with each other and to connect the communication devices with each other such as routers, switches and hubs.
Types of Networking
There are two basic types of the computer networking such as peer to peer and client/server communication. In the peer to peer communication, there is no central server and all the computers fall in the same workgroup and no central domain is exist. Such type of networking can be seen in the home or small offices where no computer server or domain controller is required. In the client/server networking model, a centralized server acts as a domain controller and it controls all the client computers in the network. All the client computers depend on the server (domain controller) for logon access, data, internet access, printer, scanner, CD-ROM, critical updates of the distributed applications and all the other data and shared resources. If the server gets corrupted or destroyed, the access of the client machines to the server stops and communication can exist from the client to the server or vice versa.
Introduction to Computer Network Protocols
The word protocol is derived from the Greek word “protocollon” which means a leaf of paper glued to manuscript volume. In computer protocols means a set of rules, a communication language or set of standards between two or more computing devices. Protocols exist at the several levels of the OSI (open system interconnectivity) layers model. In the telecommunication system, there are one more protocols at each layer of the telephone exchange. On the internet, there is a suite of the protocols known as TCP/IP protocols that are consisting of transmission control protocol, internet protocol, file transfer protocol, dynamic host configuration protocol, Border gateway protocol and a number of other protocols.
In the telecommunication, a protocol is set of rules for data representation, authentication, and error detection. The communication protocols in the computer networking are intended for the secure, fast and error free data delivery between two communication devices. Communication protocols follow certain rules for the transmission of the data.
Protocols Properties
Different protocols perform different functions so it is difficult to generalize the properties of the protocols. There are some basic properties of most of the protocols.
• Detection of the physical (wired or wireless connection)
• Handshaking
• How to format a message.
• How to send and receive a message.
• Negotiation of the various connections
• Correction of the corrupted or improperly formatted messages.
• Termination of the session.
The widespread use of the communication protocols is a prerequisite to the internet. The term TCP/IP refers to the protocols suite and a pair of the TCP and IP protocols are the most important internet communication protocols. Most protocols in communication are layered together where the various tasks listed above are divided. Protocols stacks refer to the combination of the different protocols. The OSI reference model is the conceptual model that is used to represent the protocols stacks. There are different network protocols that perform different functions. Following is the description of the some of the most commonly used protocols.
HTTP (Hyper Text Transfer Protocol)
Hypertext transfer protocol is a method of transmitting the information on the web. HTTP basically publishes and retrieves the HTTP pages on the World Wide Web. HTTP is a language that is used to communicate between the browser and web server. The information that is transferred using HTTP can be plain text, audio, video, images, and hypertext. HTTP is a request/response protocol between the client and server. Many proxies, tunnels, and gateways can be existing between the web browser (client) and server (web server). An HTTP client initializes a request by establishing a TCP connection to a particular port on the remote host (typically 80 or 8080). An HTTP server listens to that port and receives a request message from the client. Upon receiving the request, server sends back 200 OK messages, its own message, an error message or other message.
POP3 (Post Office Protocol)
In computing, e-mail clients such as (MS outlook, outlook express and thunderbird) use Post office Protocol to retreive emails from the remote server over the TCP/IP connection. Nearly all the users of the Internet service providers use POP 3 in the email clients to retrieve the emails from the email servers. Most email applications use POP protocol.
SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol)
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol is a protocol that is used to send the email messages between the servers. Most email systems and email clients use the SMTP protocol to send messages to one server to another. In configuring an email application, you need to configure POP, SMTP and IMAP protocols in your email software. SMTP is a simple, text based protocol and one or more recipient of the message is specified and then the message is transferred. SMTP connection is easily tested by the Telnet utility. SMTP uses the by default TCP port number 25
FTP (File Transfer Protocol)
FTP or file transfer protocol is used to transfer (upload/download) data from one computer to another over the internet or through or computer network. FTP is a most commonly communication protocol for transferring the files over the internet. Typically, there are two computers are involved in the transferring the files a server and a client. The client computer that is running FTP client software such as Cuteftp and AceFTP etc initiates a connection with the remote computer (server). After successfully connected with the server, the client computer can perform a number of the operations like downloading the files, uploading, renaming and deleting the files, creating the new folders etc. Virtually operating system supports FTP protocols.
What is a FTP Site:
You will learn here about FTP sites Introduction, File Transfer Protocol guide, http, https, secure sites, active mode, passive mode communication and encryption methods. FTP (File transfer protocol is a most secure way to transfer the files over the internet. The most common and simple use of the FTP is to download the files from the internet. All internet users, by this way or other use the FTP whether they know it or not. FTP is acts as the backbone of the music, games, files, movies, images and other documents download.
When you are downloading a file or data in the form of the docs or any other format, you are actually transferring the file to your computer from another computer over the Internet. You can also know the exact physical location of the serves from where you are downloading the files but you normally know the web addresses of the ftp or http websites.
An FTP address start with this prefix ftp: // while on the other hand an http address stats with this prefix http://.
A computer that gives ftp access establishes a FTP connection. A computer that is served to host the websites is known as web server similarly a computer that establish a ftp connection known as ftp server or it is also called a ftp site.
FTP site is like a large filing cabinet. As the files are properly organized in the filing cabinet and a proper name and label can be placed on the files just like same ftp files are also properly organized and named on the ftp server.
To connect to the ftp sites three things are required ftp server ip address or host name, user id and password. By providing these three things a user can be connected to the ftp sites and can download or upload the files. The administrator of the FTP sites controls the levels of the access like read only, write or full control.
When you download anything from the Internet, you are anonymously connected to the FTP with a anonymous user id. To make a FTP connection you have to use a web browser or a FTP client software like cuteftp, wsftp or aceftp. AceFTP can be get as free.
If you want to transfer the large files then you have to use the FTP clients because web browsers are not recommended to use in this scenario. If your work is of secure name like medical transcription data or any other thing then you should use the secure FTP connections with the capabilities of 64-bit SSL encryption methods. Many FTP clients have the resume features, which mean if you data is not properly uploaded or downloaded due to any reason then you can resume the connection from where it was broken. You don’t need to start the transfer again from the beginning.
What is an FTP Client?
An FTP client is a software that is designed to transfer the files over the Internet. You will have to Install it on your computer and then configure the FTP sites separately with the IP address, username and password given by the FTP hosting company. Normally a FTP client software is split into the two panes left and right. The left pane displays the files and folders of your computer and the right pane shows the files and folder of your FTP site over the Internet. Files are normally properly organized on the FTP server.
With the FTP client software the file transfer is very easy and you just have to drag and drop the files from the one pane to another. You can also transfer the file by highlighting it clicking the left or right arrow.
There are certain other features in the FTP clients software like resume feature, multiple file transfer feature, scheduling feature (automatically checks the files to be uploaded or downloaded from the client side), queuing utility, synchronize utility and the scripting utility.
Understand How FTP works.
The FTP (file transfer protocol) is used to transfer the files between the host computers. FTP works on the principal of client/server.
If you have connected to the FTP server using the Active mode you must configure your firewall in such a way that it must accept all the incoming Internet connections. Most internet service providers block the ports above 1024 because this port is used by most of the FTP clients. You can simply change the status of the FTP from the Active mode to the passive mode and then connect to the FTP server because most FTP server usually supports the passive mode.
FTP Communication: Once a connection is established between your computer and the remote computer then you can easily transfer the data in the form of files or folders or any other. In a FTP session the following two connections are made.
• The control connection is established in the form of client/server. In this scenario, the server listen to the port 21 and waits for the client connections. The client opens a port above 1023 to the server’s port 21. In this way, the client sends the commands to the server and gets the reply from the server. This connection is last as long as the FTP session is established.
• The data connection is used to transfer the data between the local and remote computer (client/server). New data connection is opened for each command sends by the client to the server. The data connection opened depends on the types of the FTP session i.e Active session or Passive.
Introduction To FTP
Here you will learn about how to transfer files with FTP program, files transfer protocol introduction, ftp software program, downloading data, uploading data, free ftp software and how to configure FTP software program. You can download files, video, images, graphics, clips, music, software and web pages with the file transfer protocol program. FTP refers both as a protocol and the software applications that are used to transfer the files. With FTP you can download data in different formats in the digital form, download music, software, voice files, web pages and other.
There are a number of FTP programs that are used for the transfering the data such as CuteFTP, AceFTP, FTP voyager. Many of the software versions are offered in the free trial form. By subscribing to the AceFTP you can use it for free.
Following are the steps required for the configuring and using a FTP program for transferring the files.
The basic instructions for using all FTP program are the same. I have provided the detail for using a FTP program in a easy form and everyone with a little compute knowledge can install and use a FTP program.
BASIC STEPS
• STEP # 1: First Install FTP software on your hard disk. You can download any FTP program of your choice. I have mentioned some of them above. After installing open the program.
• STEP # 2: Next step is to enter the host address which can be in the form of IP address or URL. For example 10.10.10.1 or www.xyz.com.
• STEP # 3: Next enter your id and password which have been provided to you by the site owners, whose services you want to use. If you have been provided with the anonymous login then your login id can be “guest” and your “email address can be your password.
• STEP # 4: If your id and password is not anonymous then enter whatever id and password is assigned to you with the remote administrator.
• STEP # 5: Next click connect to establish a connection and when the connection is established, the window on the right side of the screen represents the remote site and the windows on the left side of the screen represents the local screen.
• STEP # 6: When the connection is successfully established you will see some commands will move on in the green color in the right side pane. You will also see here remote folders, move through the remote folders and locate the file, which you want do download and use. After locating the file, simply select it.
• STEP # 7: Next move through your hard disk with the window in the left side of the screen. Now open any destination folder in your hard disk where you want to download the file from the FTP.
• STEP # 8: After selecting the remote file on the right window, drag it to the window of the left or after selecting it simply click on the left arrow once, it will automatically start downloading the remote selected file into your local folder. Most FTP programs allow you to download data in this way and if your software does not allow this method then you should consult the help file to see how to start download. When you have successfully downloaded the file, you will see a new file in your destination folder in your hard disk.
General Tips & Warnings
If the FTP administrator has set permissions then everyone can download the data using anonymous FTP. In this case you are not required for any specific login information as in most cases “guest” is your login id and “your email” is your password. On the other hand, if the permissions are not assigned to the files to be used by the general public then you must need a user id and password to access the files on the FTP site. To avoid losing the file after it has been downloaded, take a note of its name and location on your hard disk.
You can find it later by using the Find function of Windows and by using the Run command. If you have permissions to delete the remote files then you must not delete the files in the FTP site, unless you make sure that the downloaded data are accurate and downloaded 100%.
Otherwise, after deleting the remote files you may find some difficulties to access those files if they were not downloaded properly. You will have to request your host to re-upload those data files so that you can download them once again. If you data is of some secure nature like official files, medical transcription voice files or others then your FTP host must have the capability for 128 bit encryption. In this way, the files will be transferred in the encryption and secure form and there will be no chances of hacking or losing of the information.
Some good software automatically delete the voice files in the FTP sites after successfully downloading them to you hard disk. These software also make a archive (log) of all the downloaded data. So there are no chances of missing a file. GearXport is one them and it is used for downloading the voice files for the medical transcription work.
IP (Internet Protocol)
An Internet protocol (IP) is a unique address or identifier of each computer or communication devices on the network and internet. Any participating computer networking device such as routers, computers, printers, internet fax machines and switches may have their own unique IP address. Personal information about someone can be found by the IP address. Every domain on the internet must have a unique or shared IP address.
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol)
The DHCP or Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol is a set of rules used by a communication device such as router, computer or network adapter to allow the device to request and obtain and IP address from a server which has a list of the larger number of addresses. DHCP is a protocol that is used by the network computers to obtain the IP addresses and other settings such as gateway, DNS, subnet mask from the DHCP server. DHCP ensures that all the IP addresses are unique and the IP address management is done by the server and not by the human. The assignment of the IP addresses is expires after the predetermined period of time. DHCP works in four phases known as DORA such as Discover, Observe, Request and Authorize.
DHCP Overview
In this section you will learn the DHCP router overview, dynamic host configuration protocol overview, network tutorials, troubleshooting tips, subnetting, IP addressing. DHCP or Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol is a network protocol, which is configured in such a way that is provides the IP addresses to the network computers automatically. There is no need to assign the IP address to the client computers individually. DHCP assigns the IP addresses from the given range of the numbers also called DHCP scope.
On the other end, client computers are configured in such a way that they get the IP addresses automatically from the DHCP server during the boot up process. Additionally, DNS and WINS servers can also be configured with the DHCP server.
When a computer starts up it gets the IP addresses from the DHCP server from the defined pool of addresses.
The assigning of the IP address by the DHCP server can be categorized as follows: 1. A user turns on the computer with the DHCP client enabled on it.
2. The client PC sends broadcast request (known as DHCP DISCOVER) and then look for the DHCP server to answer.
3. The DHCP server receives the DISCOVER packet and based on the availability and defined settings, the server choose any available IP address and then give to the client. Then DHCP server sends back to the client with DHCP OFFER with that available address information.
4. Again client sends a request to DHCP server known as DHCP REQUEST, in which it lets the server know that it is using the address offered by the DHCP.
5. The DHCP server then again send a acknowledgement to the client known as DHCP ACK, in which it confirm the client that the specific IP address has been assigned to it for a given period of time.
This process of assigning the IP addresses by the DHCP server also known as DORA (Discover, Offer, Request, and Acknowledgement).
When a computer uses a static IP address there can be the chances of error and conflict when two computers use the same IP address. By using the DHCP server there are no chances of such kind of conflicts and errors.
Along with the IP addresses, the DHCP server also enables the client computers to extract all the settings and configurations from the DHCP server on an IP network. These settings include the Firewall, Router, DNS, NAT, WINS, Gateway and Subnet masks settings.
The overall purpose of the DHCP server is to reduce the workload and error margins, which can occur in assigning the IP addresses manually.
The IP address assigned by the DHCP server is for the limited or leased period of time and if a client needs an to extend that leased period for the IP address then client must send a extension request to the DHCP server before this period expires. If the client do not send an extension request, then this IP address becomes free on expiration and is assigned to another client. If a user wants to change the IP address given by the DHCP server then he/she do it by giving these commands on the command prompt.
“IPconfig/release then IPconfig/renew”.
This command will remove the current IP address and assign a new IP address to the client.
There can also be some reserved addresses based on the MAC address or hostname of the client. These reserved addresses are fixed addresses and can only be assigned to the fixed clients.
How to Setup a DHCP Server?
The installation of the DHCP server in the Windows 2000 or Windows 2003 is quite easy. You can install the DHCP server by using the “Manager Your Server Wizard”.
Open Manager Your Server wizard and select the DHCP server option and press next then you will be asked to enter the name and the description of the DHCP scope.
A scope is a collection of the IP addresses on subnet that use DHCP. In the next window you will be asked to define the range of the IP addresses and the appropriate subnet mask that DHCP server will distribute across the all network. Next you will see a window in which you can add anyIP address, which they don’t want to use because these are already in use for example 100.100.100.10 is an IP address of the company’s router and you don’t want that DHCP server use this address and assign to some other client.
So you can add these addresses in the exclusion field. You can define fix range of the IP addresses for exclusion. In the next step you have to assign the lease duration this means that for how long a client can use the IP address, which it got from the DHCP server. You can assign any lease duration. 10 hours, 1 week, 1 month or 1 year so on.
Next you will be asked to configure the scope of the DHCP options now or you can also configure it later.
Next the DNS and the domain name configurations and settings can be entered. The IP address of the DNS server will be assigned and distributed by the DHCP server.
Next if you have WINS requirements then you can enter the IP address of the WINS server. You can just type the server name into the box and then press resolve it will automatically resolve the name of server and find the IP address.
The next step is to activate the scope in the DHCP server because the DHCP server will not work until and unless you activate the scope. The DHCP server is now installed and you can modify the settings according the structure and the requirements of your network.
Make a plan according to the needs of your network before using the DHCP server.
IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol)
The Internet Message Access Protocol known as IMAP is an application layer protocol that is used to access to access the emails on the remote servers. POP3 and IMAP are the two most commonly used email retrieval protocols. Most of the email clients such as outlook express, thunderbird and MS outlooks support POP3 and IMAP. The email messages are generally stored on the email server and the users generally retreive these messages whether by the web browser or email clients. IMAP is generally used in the large networks. IMAP allows users to access their messages instantly on their systems.
ARCNET
ARCNET is a local area network technology that uses token bus scheme for managing line sharing among the workstations. When a device on a network wants to send a message, it inserts a token that is set to 1 and when a destination device reads the message it resets the token to 0 so that the frame can be used by another device.
FDDI
Fiber distributed data interface (FDDI) provides a standard for data transmission in a local area network that can extend a range of 200 kilometers. The FDDI uses token ring protocol as its basis. FDDI local area network can support a large number of users and can cover a large geographical area. FDDI uses fiber optic as a standard communication medium. FDDI uses dual attached token ring topology. A FDDI network contains two token rings and the primary ring offers the capacity of 100 Mbits/s. FDDI is an ANSI standard network and it can support 500 stations in 2 kilometers.
UDP
The user datagram protocol is a most important protocol of the TCP/IP suite and is used to send the short messages known as datagram. Common network applications that uses UDP are DNS, online games, IPTV, TFTP and VOIP. UDP is very fast and light weight. UDP is an unreliable connectionless protocol that operates on the transport layer and it is sometimes called Universal Datagram Protocol.
X.25
X.25 is a standard protocol suite for wide area networks using a phone line or ISDN system. The X.25 standard was approved by CCITT now ITU in 1976.
TFTP
Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) is a very simple file transfer protocol with the very basic features of the FTP. TFTP can be implemented in a very small amount of memory. TFTP is useful for booting computers such as routers. TFTP is also used to transfer the files over the network. TFPT uses UDP and provides no security features.
SNMP
The simple network management protocol (SNMP) forms the TCP/IP suite. SNMP is used to manage the network attached devices of the complex network.
PPTP
The point to point tunneling protocol is used in the virtual private networks. PPP works by sending regular PPP session. PPTP is a method of implementing VPN networks.
OTHER PROTOCOLS
VTP, ARP, IPX, OSPF, RARP, NFS, BOOTP, NNTP, IRC, RADIUS, Soap, Telnet, RIP, SSH.
Network Management Overview
During the lifecycle of a computer network, it faces complexities that need to be solved. As an organization becomes increasingly dependant on the computer networking services, keeping these services running accurately are necessarily required for the smooth operations within an organization. Network management is a procedure in which a computer network is operated, configured, secured, troubleshoot, monitored and maintained by means of management/monitoring tools and techniques and network administrator is responsible for accomplishing the administrative tasks. Managing a computer network involves a number of tools, applications, devices and techniques. The level of management increases as our network expands and new technologies, devices and services are added in our network such as VOIP, ISDN, Packet switching, circuit switching, routers, clustering, centralized storage, firewall software/hardware and video streaming. Automating the tasks such as logs generating, alerts, scheduled downloading/uploading, virus scanning, bandwidth monitoring and printing certainly provide ease in the administrative and network management tasks of the network administrators.
There are certain software that can be used to manage the computer network such as Nsauditor Network Security Auditor, IPSentry Network Monitoring Suite, LanGuard, Alchemy Eye and Network Administrator's Toolkit. In the LAN/WAN network management model there are six key areas that need to be discussed.
Fault Management
Fault management is carried out automatically or through network administrator’s manual work. The purpose of faulty management is to keep logs, isolate the problems and troubleshoot them in a timely manner to keep the computer network running smoothly and effectively.
Security Management
Security management includes securing the network resources, applications and devices from the unauthorized access. Security management also includes implementing the security policies, configuring the firewall, intrusion detection, preventing virus attacks and securing the network from internal and external threats by securing management tools and techniques.
Performance Management
Performance management includes the various aspects of the network performance to maintain the good and acceptable performance in a computer network.Configuration ManagementConfiguration management monitors the configurations such as TCP/IP, operating system, SMTP, DNS, DHCP, FTP, Firewall and network devices such as LAN card, switch and router, in a computer network. All the configurations can be stored in a centralized database for quick access and these configurations provide help while troubleshooting the problems.
Accounting Management
Accounting management involves the utilization of all the network resources. Controlling the network utilization helps in preventing the problems such as delay in network response and bottleneck. Measuring the network resources utilization is helpful in allocating usage quote of the network resources and in providing the optimized performance to all the users.
Application Management
Application management involves the fast deliver of the applications to the network users. You can prioritize application traffic, control bottleneck and accelerate the performance of the applications.
The other functions that are the part of the computer network management includes planning, deploying, configurations, coordinating, troubleshooting, monitoring the network resources, traffic routing, load balancing, cryptography, authorization, bandwidth management and security management.
Network Management System
In a big computer networks the centralized management of a network is required to monitoring, planning, allocating, security, deploying, coordinating and configuring the computer network. Network management means managing the administration and security, risk, reliability and performance of a network over a very large scale. There are different software and hardware components are available to manage the computer network locally or remotely.
Being a network administrator or IT manager, you have to ensure the security of your computer network i.e. your network is protected from the unauthorized users and from hackers. For this purpose you have to restrict the user rights, implement the securities policies, use firewalls and monitor the network traffic and performance with the different tools. Some high end software produces real time graphical views to monitor the network activities.
As the network expand the maintenance policies and strategic growth planning is required to manage the network.Network management architecture depends on the client-server relationship i.e. some software applications are installed at all the workstations and all the activities of the workstations are monitored at the server. When a system alert is received at the server, certain actions such as event logging, system generated messages to users and system shutdown is performed.
The protocols that are involved in the management of a network are simple network management protocol SNMP and common management information protocol CMIP. ISO has contributed to a large extent in making the standards of managing and administering a network. The management of a computer network involves certain things such as security, risk, performance, fault, system, accounting, configuration load balancing, and traffic routing and traffic management. The purpose of the performance management is to measure the performance such as the user’s response time and application performance.
When a certain performance threshold is reached, a system alert is generated and sent to the server and it is monitored and certain actions are performed in response of it. Security management is to secure the network from the unauthorized users and also secure the resources and sensitive data. Certain security policies and security systems are enabled to ensure the security of the network. The purpose of the fault management system is to track records of the faults, isolate faulty software or hardware and fix them. There are certain network management systems and software being used for optimizing the maximum resources allocation, reporting capabilities, real-time fault detection and reduces the network downtime.
This software provides the comprehensive management features such as for monitoring, analyzing, managing, fault detection and security. Using a good network management system reduces the workload of the IT support staff, measure the network performance and provide the real time statistics of all the computers in a network. Certain software is used to keep track of the bandwidth usage of network and the tracked information is stored in the centralized database for analysis and monitoring. Through this data you can analyze the bandwidth requirements of your network and can plan for the increase in bandwidth.
A good network management system ensures that a network is being used efficiently and it provides organization’s productivity, security, scalability and flexibility. For the flexible working, businesses should deploy a good centralized network management system so that employees can provide timely reports, coordinate with colleagues and perform their duties effectively. Make sure your network is secured by installing firewall software
Introduction to Internet :
In this basic internet tutorial you will learn about web browsing, world wide web, http, online shopping ftp, routing and online communication system. Internet is a network of publicly available networks. The internet was first developed in 1969 and was known as ARPAnet, by the US department of defense. Initially only were computers were interconnected and the aim of the DOD was to make a nationwide network of computers to share the information in the times of War and emergency. The internet was available for the public for the first time in 1992 and many big internet companies came into existence after that time.
Internet is an electronic network of the computers across the globe, which is interconnected with each other. Millions of the computers are the part of the internet around the world such as telecommunication computers, military computers, airlines computers, universities computers and other commercial computers.
The most common use of the internet is the World Wide Web (WWW) and the most important feature of the WWW is HTTP (hypertext transfer protocol). This protocol is used to view the html documents in the web browsers. TCP/IP (transmission control protocol/internet protocol) is the protocol that is used for communication in the internet. Every computer which is connected with the internet has a unique identifier which is known as IP address. An IP address is a 32 bits decimal numbers address such as 10.11.11.1, 112.1.1.30 etc.
There are certain types of the features on the internet such as web browsing, emails, Telnet, FTP, Gopher and other features. Today every kind of information is available on the internet and is accessible in seconds. We can share html web pages, songs, videos, games, graphics, news and other types of applications. Internet has become a big business portal for almost every kind of business in the world. Almost every well known company in the world has it presence on the internet.
There are certain marketing methods on the internet that are used to promote a business such as search engines marketing methods, email marketing, banner exchanges, directory submission, articles writing and promoting and many other types. Today researches can share their knowledge and experiences with their fellow researchers around the world, which was not easy before the internet. Internet is also a source of distance learning education system, in which a student is enrolled in a specific course on the internet, no matter what the geographic location of the student is. Internet connection is easily available to everyone who has a computer, fax modem and a telephone line. Upon connecting with the local ISPs, we can connect with every available computer on the internet.
There are certain other advantages of the internet such as video conferencing, telemarketing, telemedicine, call centers, VOIP and web conferencing. Advance education and new research was not available so fast to everyone before the internet. The communication on the internet is carried out by a device known as a router. A router is a communication device which has a built inn routing table and with this routing table the destinations of the data is determined. Routing on the internet is a method of communication that uses physical address, selection of the gateway and the numerical address of the computer or routers.
Technically, internet is consisting of a large number of the interconnected autonomous systems. The most commonly used protocols by the routers are RIP and OSPF. Both the packet switching and IP networks provide the way, which routing protocols use for the communication on the internet. There are certain dedicated computers on the internet that are available online 24 hours and provide certain types of services. Internet also facilitates us for online bookings in the airlines and trains. Many companies uses internet as a medium to connect with the other private networks of the same company. Many universities and colleges use internet to form their private intranet, in which only authorized persons can access the private resources of an organization or university.
Finally, internet is a largest learning and information sharing portal on this planet in which many people from all over the world get connected with each other at the same time and can communication in a number of ways.
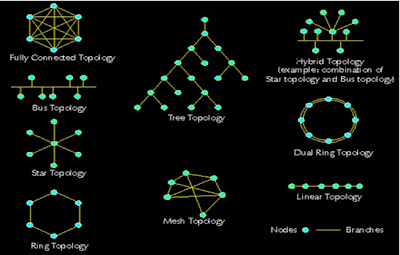
Thank You ! and I always welcome your invaluable suggestions to improve my articles .
Sourabh Banerjee ,INFI-NITE,Ranchi
No comments:
Post a Comment